Case study on the use of self-service kiosks in supermarkets

- CompanySelfmarket
- RoleProduct Designer
- Duration1 month
- Responsibilities
- Conduct user research
- Create wireframes and prototypes
- Collaborate with developers
With the advancement of technology, more and more supermarkets are using self-service systems as they are theoretically faster and lower cost. This case study focuses on analyzing the impacts and problems arising from the implementation of these systems and proposing a solution to make the experience more pleasant and accessible.
Mobile application with payment integration and self-service features. Accessible for visually and motor-impaired users, focusing on usability and efficiency.
Understanding the problem
Current scenario
The supermarket checkout automation model or self-checkout originated in the United States and has been gaining more strength in recent years, being widely used worldwide today.
With the arrival of the pandemic, this model was one of the alternatives that has been used with greater force in the global market, bringing a very large impact on people's lives.
The challenge for the entrepreneur who did not use this model was not easy, in addition to having to restructure the team, perhaps the physical space, migration to online, among others.
CSD Matrix
In structuring the Matrix, consideration was given to what methods/research would be used later so that assumptions and doubts could be validated.
- Many people will become unemployed;
- People will have difficulty scanning items;
- The employer will have reduced operational costs.
- Visually and/or motor impaired people will have difficulties making purchases autonomously
- Illiterate people will have difficulty making purchases autonomously
- The supermarket will have reduced queues with checkout automation
- The user will have more privacy when making their purchase
- Greater sales capacity offered by the retailer
- What pains do users who use an automated system face today on a daily basis?
- Will the amount of theft and robbery of products increase?
- Would users use an app to place orders?
- Would an app solve the problems faced by users today?
- People who don't use self-checkout systems, why don't they use them?
- Will people resist using an artifact to acquire products autonomously?
Desk research
The research involved analyzing market trends, case studies, expert reports and secondary data from various sources, with the aim of understanding best practices, emerging technologies and challenges faced by companies that have already implemented this solution.
The main objective was to identify critical success factors, evaluate the impact of this technology on service and explore improvement opportunities for the project in question. Based on the findings of this research, it will be possible to base strategic decisions that enable the creation of an efficient solution aligned with user needs and organizational objectives.
- 60,4% of Brazilians prefer the self-checkout system. (Mercado & Consumo Magazine)
- 60% report long queues as the main pain point. (Forbes)
- 85% believe that self-checkout is faster than the traditional model. (Forbes)
- 73% of respondents are in favor of self-service / self-checkout. (Forbes)
- 87% of people opt for contactless payment or self-checkout. (Forbes)
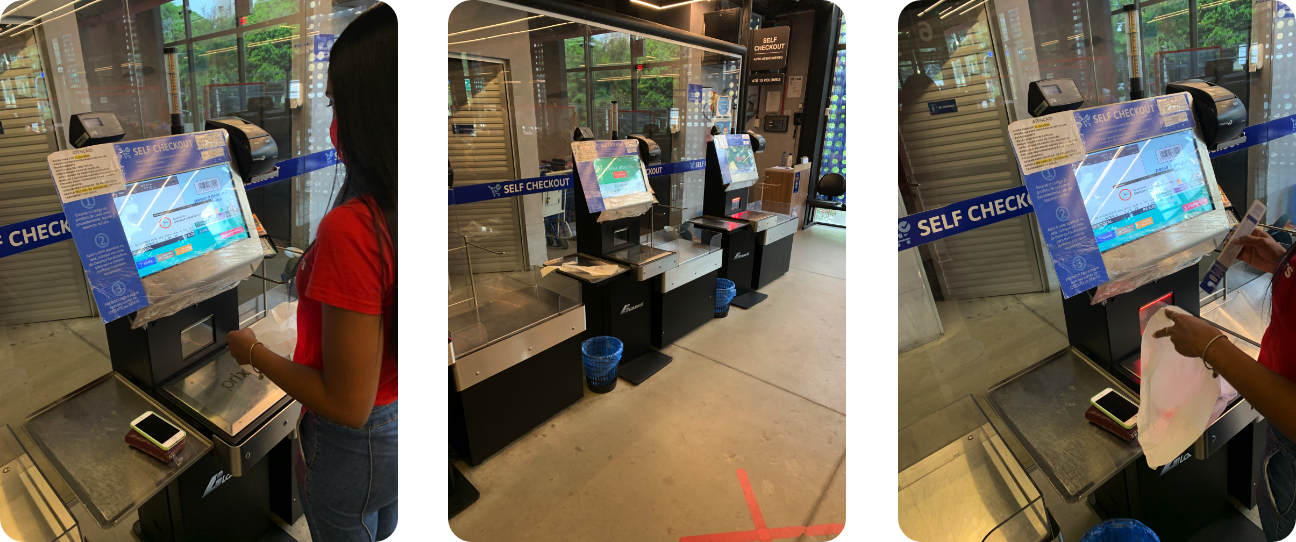
Shadowing
Through the research, it was possible to observe some pain points faced during the use of a self-service kiosk / self-checkout, the steps the user takes and points of attention when it comes to accessibility and technical limitations.
- The research was conducted with users aged 20-50 years. It was not possible to observe people with motor and/or visual disabilities during the research period.
- Research location: Recibom — Av. Rui Barbosa (Graças)

Observed pain points:
- Difficulty reading barcodes;
- Scale not accounting for product weight;
- Purchase limitation of up to 15 items;
- Limitation of payment methods;
- System with freezes and slowness;
- Failure in signaling the kiosk when it's free, occupied or in use to facilitate queue flow.
Observed attention points:
- No accessibility option was observed for increasing contrast or typography size;
- No screen reading option was observed for use by visually impaired people
- Device only with touch screen, without any mechanical key interaction to facilitate use by visually impaired people
Qualitative and quantitative research
With the execution of the research, it was possible to obtain responses from 75 people who have had some experience using self-service kiosks in supermarkets. Resulting in the following metrics:
- of people used self-service for practicality
- 68,3%
- of people who used self-service to avoid queues
- 81%
- of people are between 25 and 35 years old
- 60,3%
- of people who used self-service had problem(s)
- 52,4%
- of people reported having problems with freezing
- 31,3%
- of people reported having had problems with product identification
- 24,1%
Reported problems:
- Freezing / slowness;
- Product not recognized;
- Item duplication;
- Lack of clarity on how it worked;
- Weighing failure (broken scale);
- Payment failure;
- Problem canceling item.
Analyzing results
The impact on society
Supermarket checkout automation systems have been growing significantly and bring some impact points for companies, requiring restructuring of operational positions, for example.
Among the impacts, most are positive, bringing as main points: reduction in operational costs, agility in purchasing processes and increase in sales volume.
Even with so many positive points for the employer and user, something that remains as a warning point are some technical problems in self-service kiosks and the lack of accessibility due to being touch screen devices.
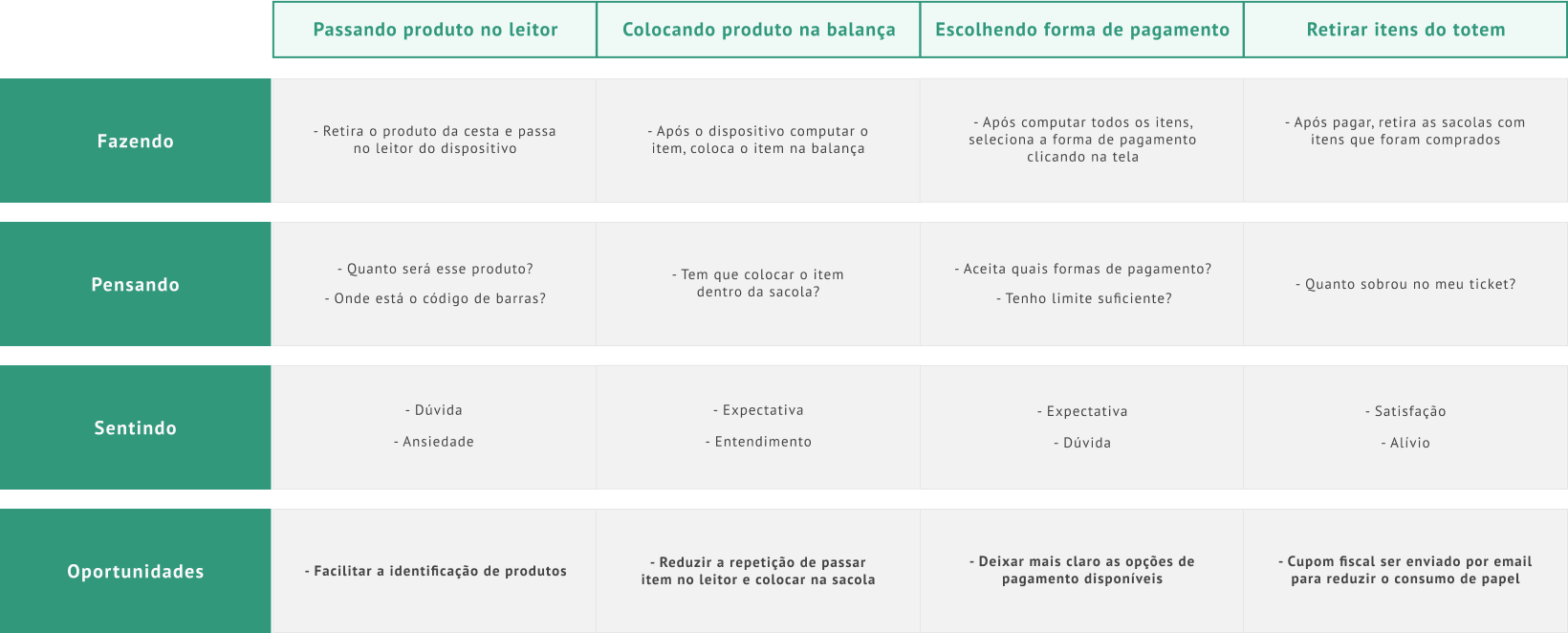
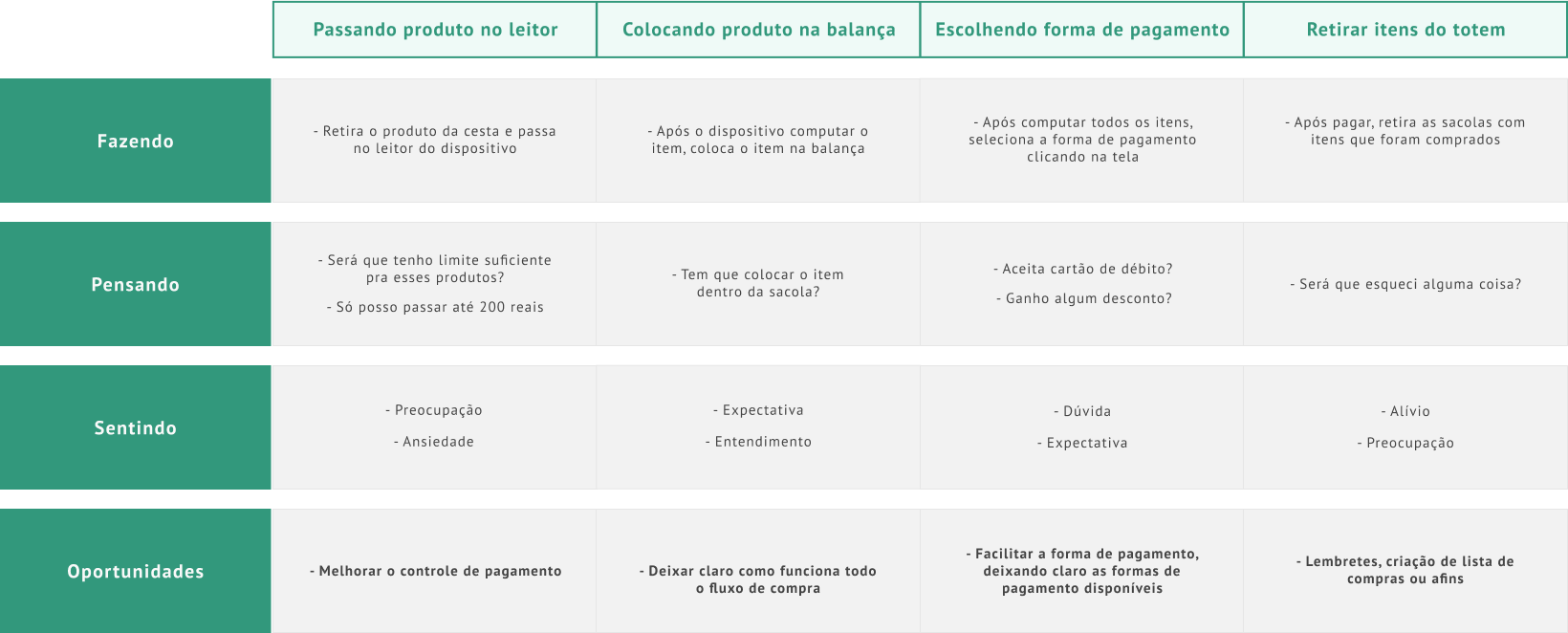
Mapping users
With data from the research, personas and journey map were created with the intention of identifying opportunities to be explored in the next stages of the process:


Idealizing the solution
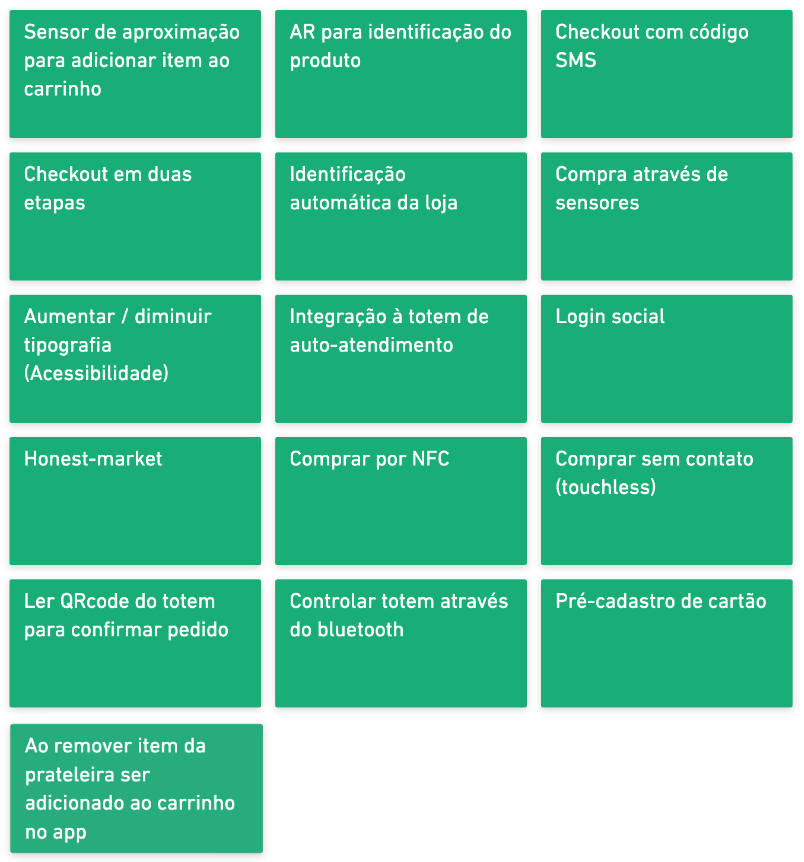
Brainstorming
Using unstructured brainstorming, possible points to be considered in idealizing the solution for the previously identified problems were raised:
Effort x impact matrix
Through the effort / impact matrix, it was possible to refine the ideas originated from brainstorming, with this it was possible to determine a possible solution with greater viability.
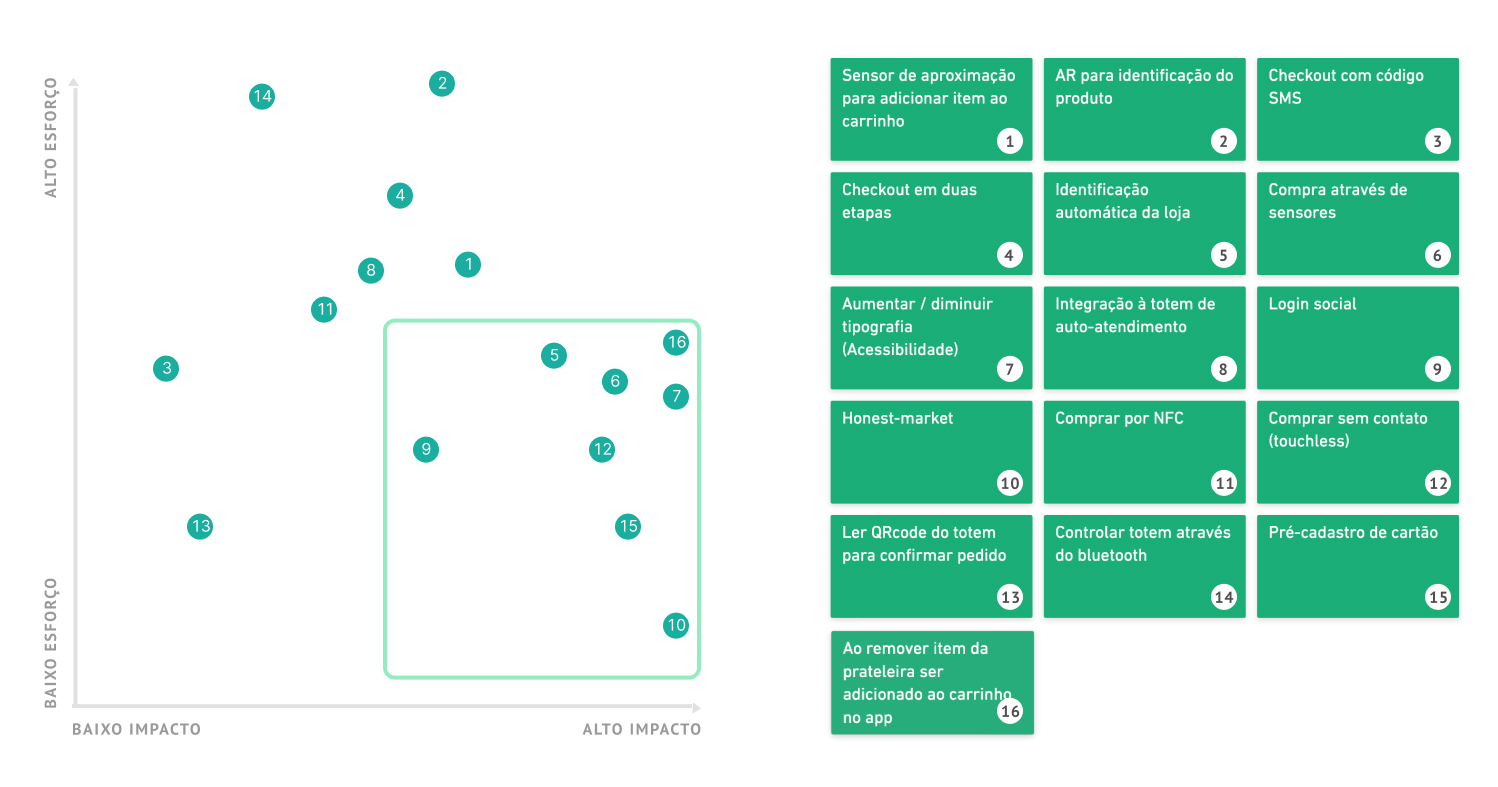
Idealizing the solution
Through research, it was identified that self-service kiosks have some technical and accessibility problems, therefore, aiming to facilitate users' lives and focusing on accessibility, it was seen that the most efficient way of operating with self-service / self-checkout system will be through the creation of an artifact aiming at the following functionalities:
- Acquire product quickly;
- Be able to pay through the app;
- Not having to face queues;
- Accessible for people with disabilities through the device's own resources, such as screen reader;
- Use the Honest market practice.
Taking into consideration the resources and functionalities necessary for it, the artifact that would become most viable will be the creation of a mobile application.
Mind map
The practice was used to organize the solution structure in a faster and more efficient way:
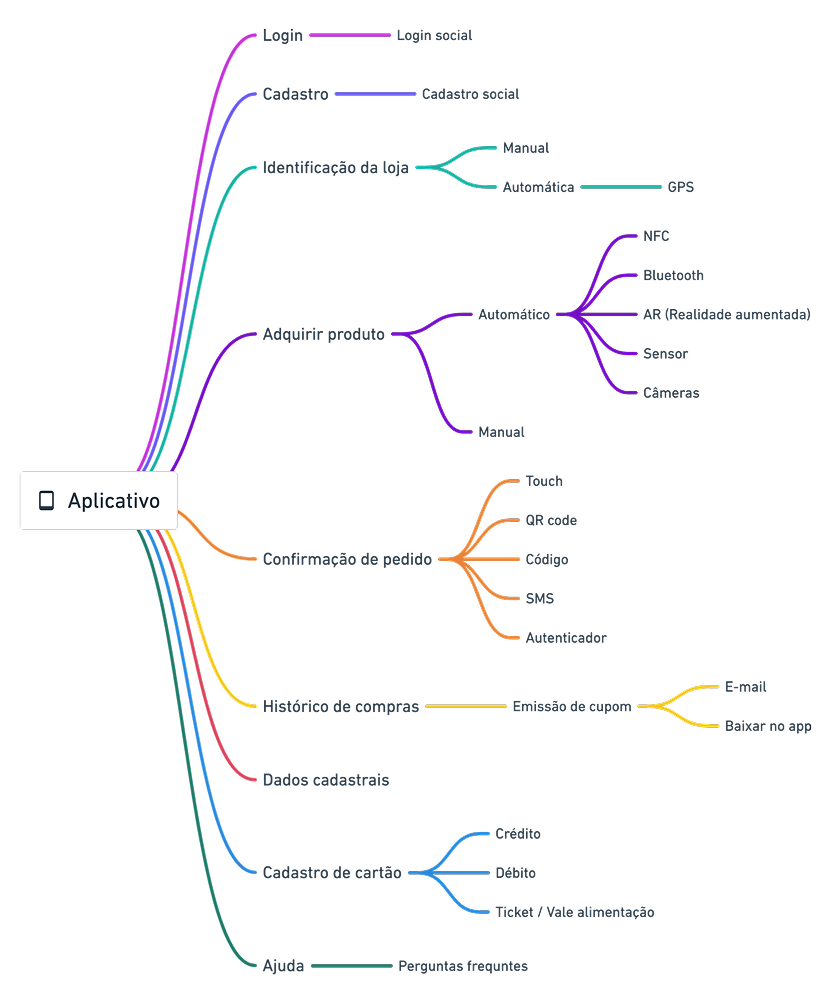
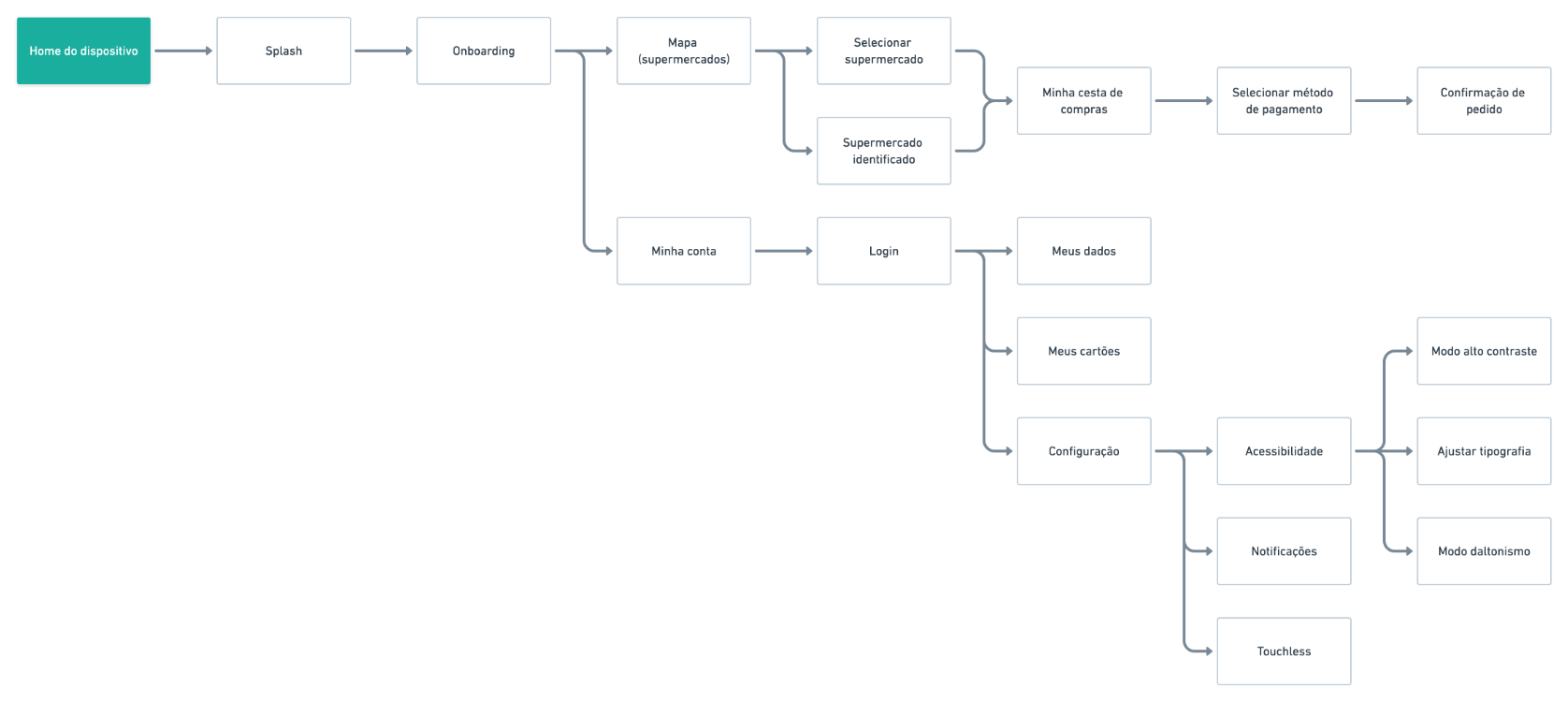
User flow
After the mapping and organization created in the Mind map, at this stage the user navigation flowchart was created:
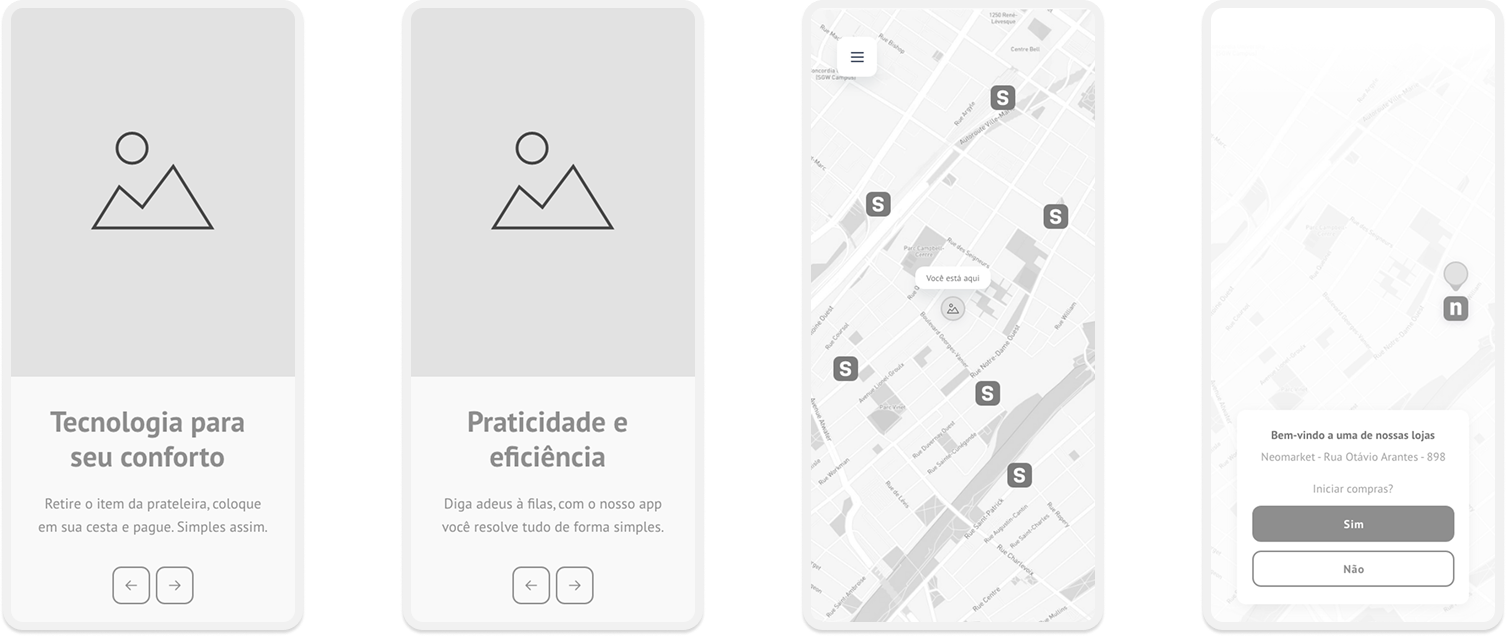
Low fidelity prototype
After building the flow, the prototyping stage was initiated. At this first moment, low fidelity screens were idealized as they are faster to validate an initial idea:

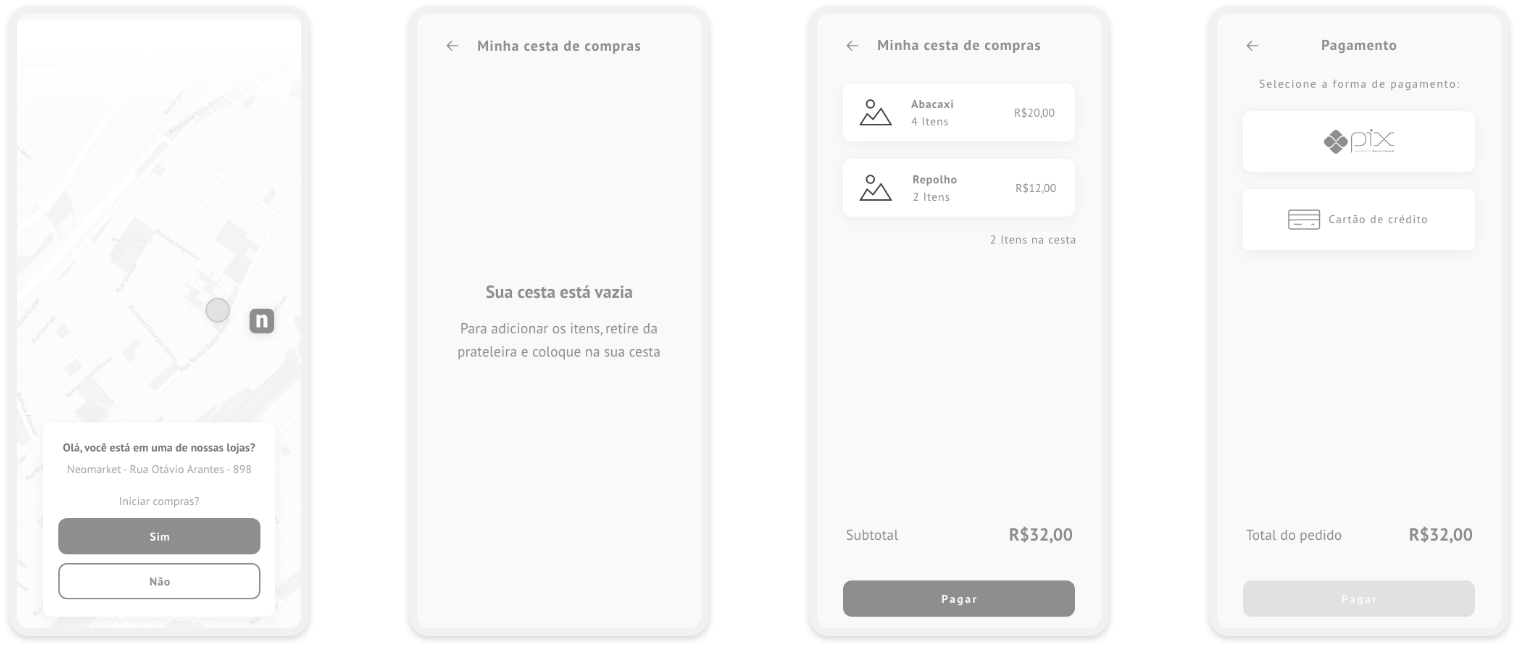
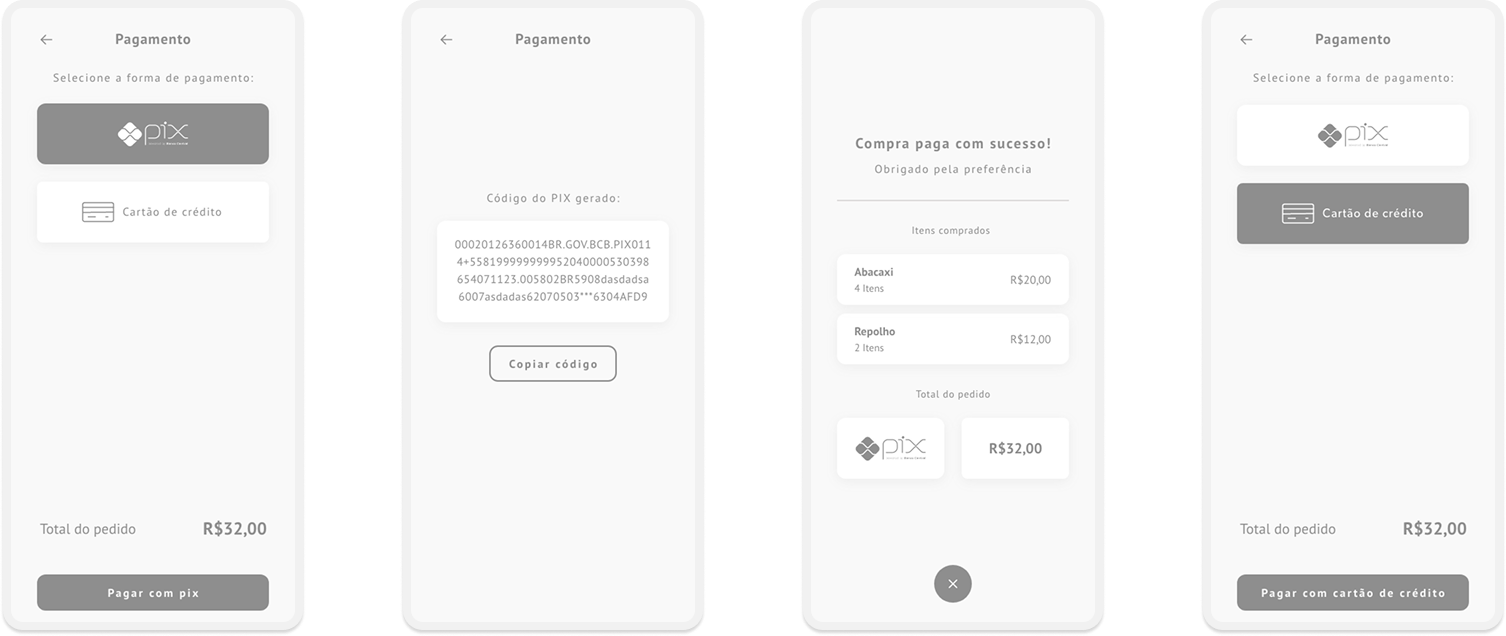
Complete low fidelity prototype:
Acessar link do protótipo interativo
Usability tests
Some usability tests were executed on the low fidelity prototype, from which some flow and writing errors were observed. Subsequently corrected in the high fidelity prototype.
Test planning:
- Definition of activities to be tested;
- Recruitment of users who resembled the personas;
- Creation of the script detailing what would be the "success" of the selected activities for testing.
Metrics analyzed in the tests:
- Completion rate;
- Complexity rate;
- Execution time
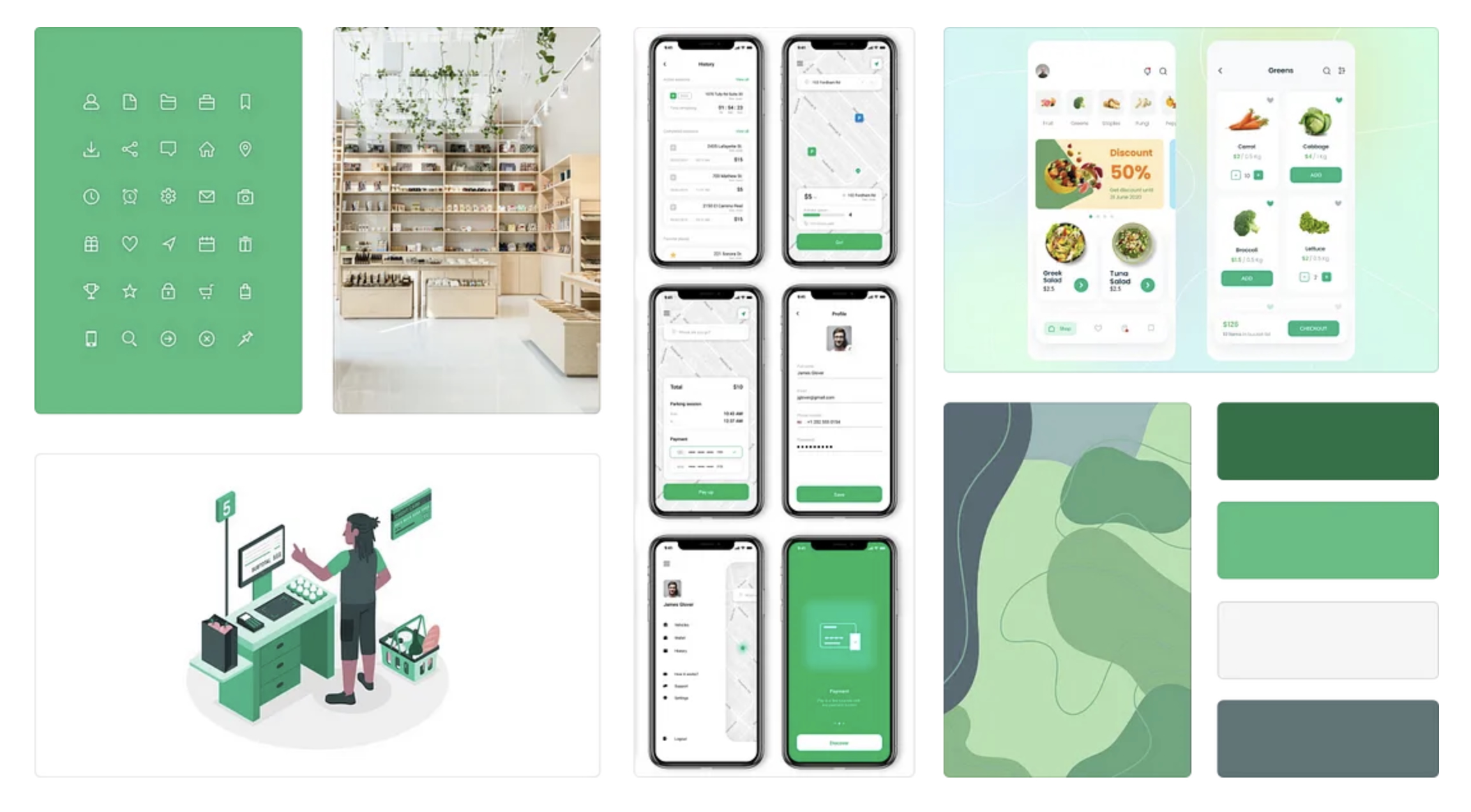
Moodboard
To contextualize the entire visual identity of the application, a board was created to be followed as an aesthetic / visual model for creating the styleguide.
Styleguide
To contextualize the entire visual identity of the application, a board was created to be followed as an aesthetic / visual model for creating the styleguide.


High fidelity prototype
Taking into consideration the styleguide and insights from usability tests, it was possible to structure the high fidelity prototype:
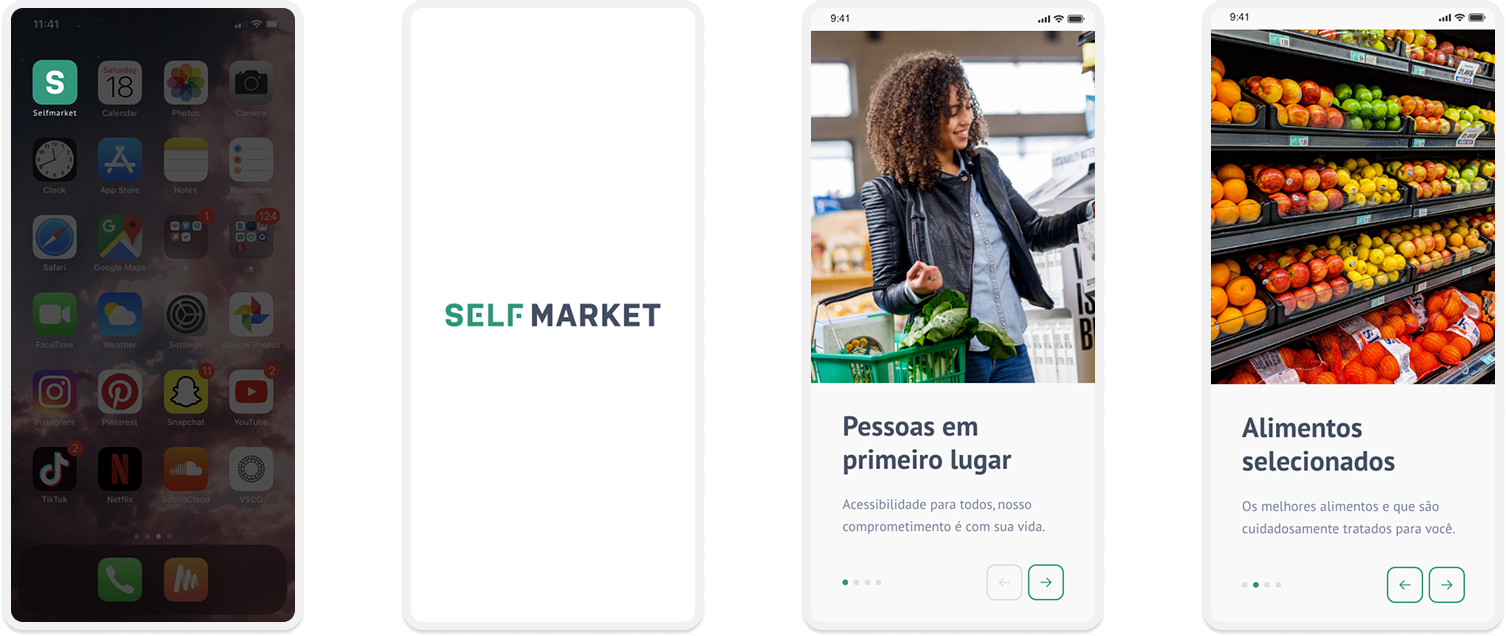
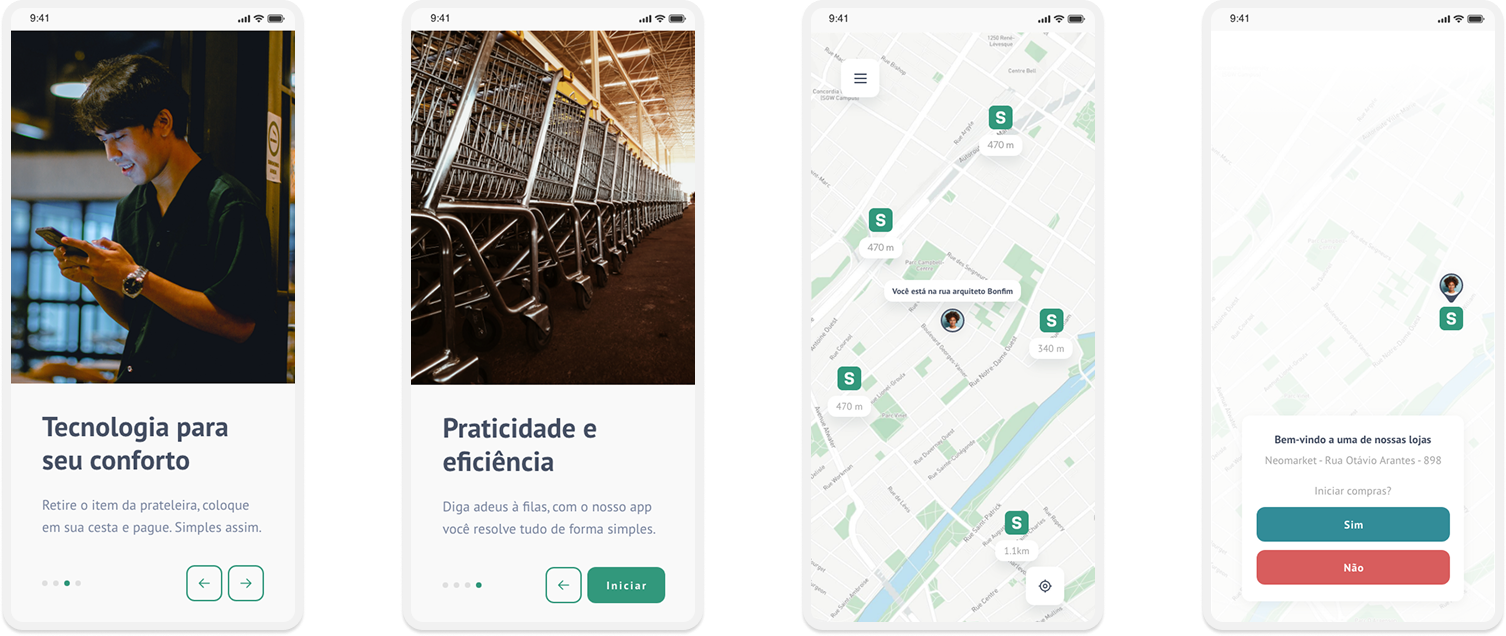
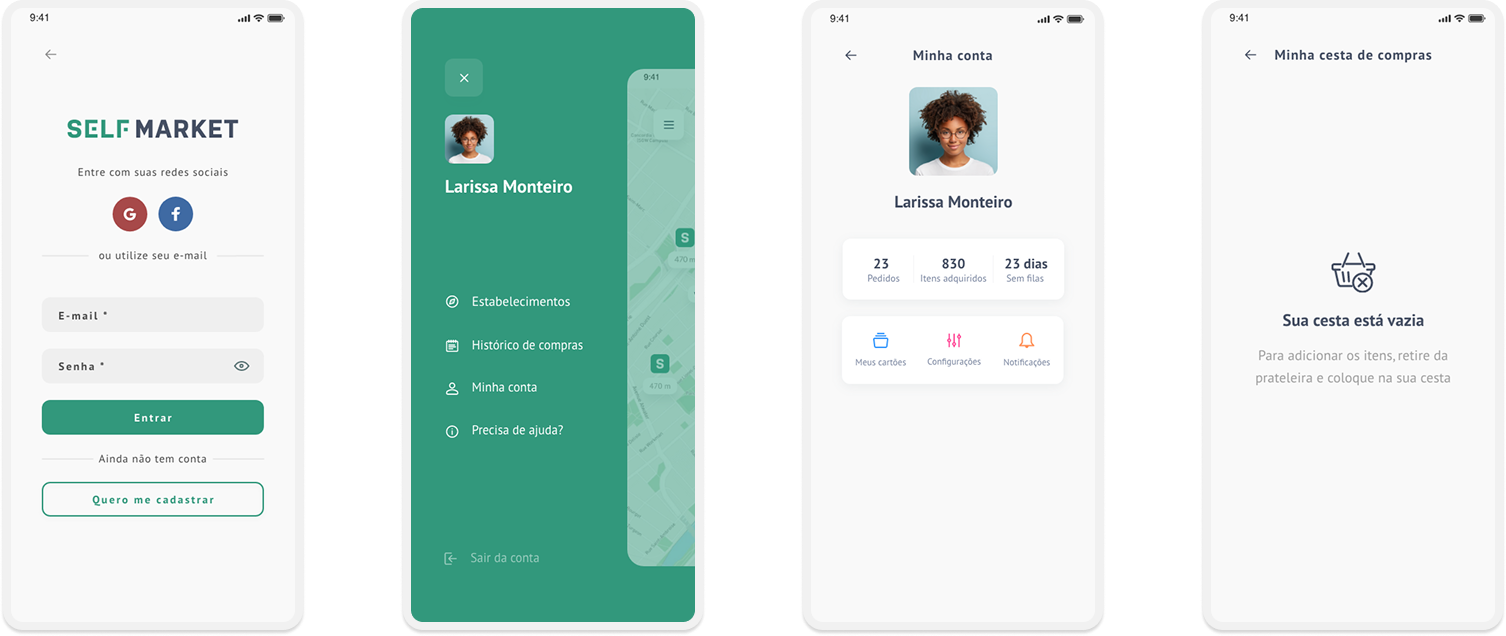
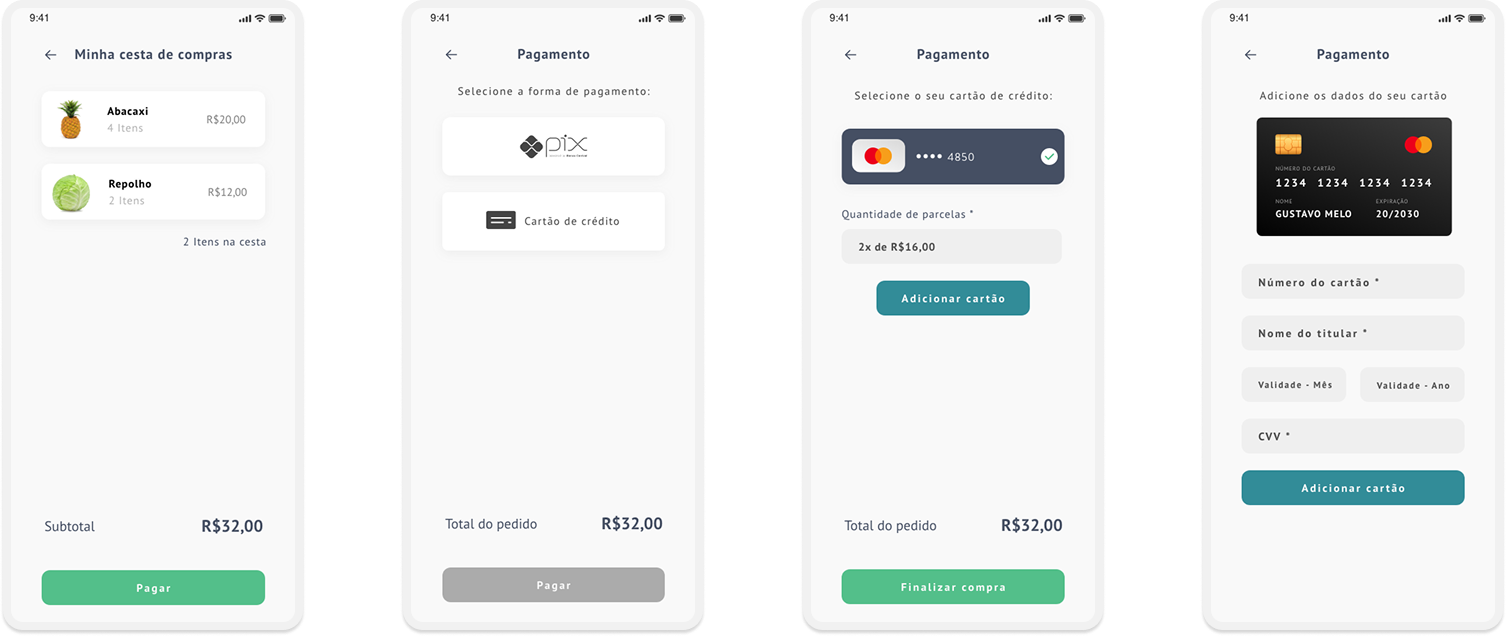
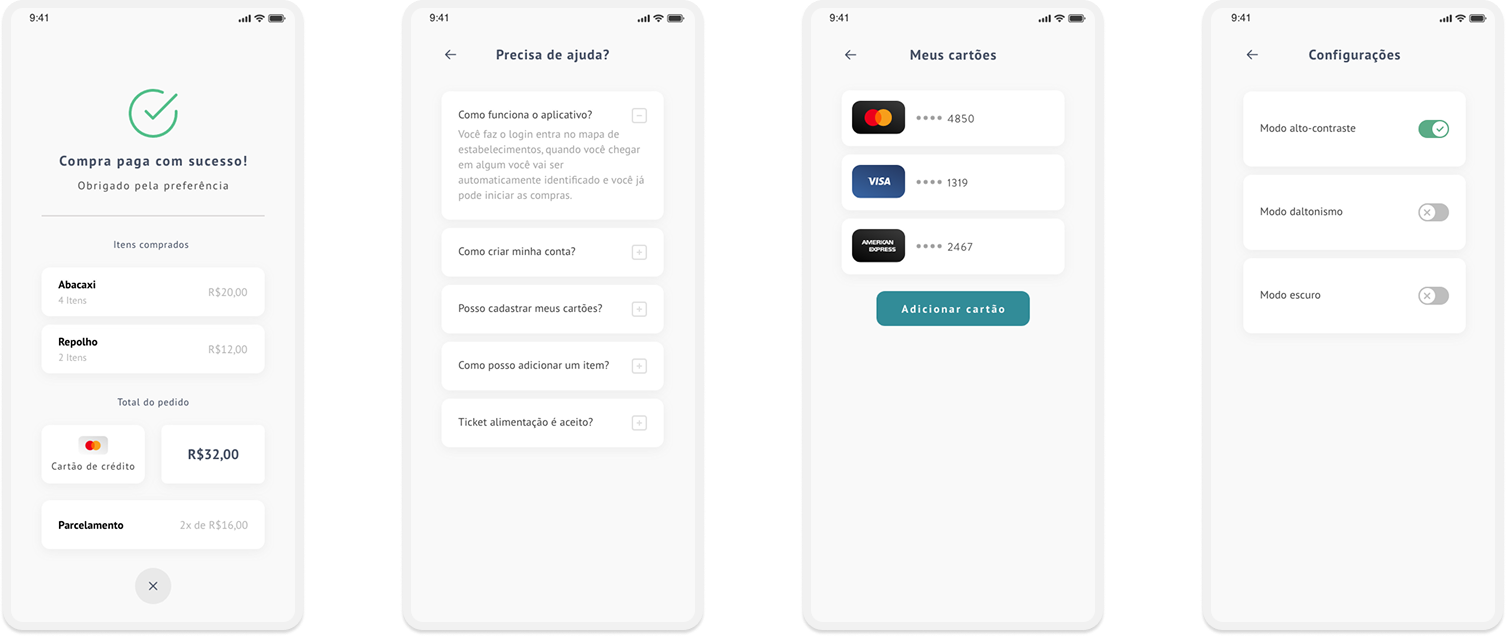
Complete high fidelity prototype:
Conclusion and learnings
In carrying out this case study, it was possible to verify improvement points in the supermarket user experience and identify the social impacts of implementing self-service systems.
Using the Shadowing practice, it was possible to closely observe the real experience of users and see the frustration of some people when using self-service kiosks.
The research stage was essential to identify the real pains of users and assist in the decision-making process for the later stages.
You can see the complete case presentation through the link below:
Next project
Case study on structuring an artificial intelligence platform for legal petitions