Case study on structuring a learning platform in the legal and public exams field
- CompanyCERS
- RoleLead Product Designer
- Duration4 months
- Responsibilities
- End-to-end management (discovery and delivery)
- Market analysis
- User research
- User mapping
- User flows
- Prototyping
- Usability testing
With the arrival of the pandemic, the face-to-face model was affected in several ways, causing many companies, professionals, and students to migrate to distance learning. The competition increased, making it necessary for platforms to evolve in terms of engagement, usability, accessibility, interface, performance, and many other aspects.
Web platform and mobile application focused on adaptive and comprehensive learning for courses in the legal field and public competitions. Providing a personalized and accessible learning experience for all users.
Understanding the problem
The context
In a scenario of consolidation of remote learning, the challenge was to offer a more fluid, personalized, and efficient digital learning experience that would increase student engagement and retention.
where the student could track their progress, access content more quickly, integrate different products (subscriptions, single courses, events), and have a clear view of their academic performance.
The current scenario
Distance learning has become a fundamental part of formal and corporate education, ceasing to be an alternative to become a strategic choice. Driven by the COVID-19 pandemic, EAD platforms have evolved and started to incorporate more sophisticated technologies, focusing on user experience, engagement, and personalization.
Main characteristics of the scenario:
Hybrid model as dominant:
Educational institutions adopted hybrid formats, combining face-to-face classes with digital content, taking advantage of the flexibility of EAD without giving up human contact.
Growth of EdTechs:
The global educational technology market continued to expand, with startups offering solutions focused on microlearning, gamification, personalized learning paths, and artificial intelligence applied to education.
Focus on student experience:
Platforms began to invest more in usability, accessibility, mobile-first, and real-time monitoring of student performance.
Artificial Intelligence and data analysis:
AI began to be applied in content recommendations, virtual tutors, automatic corrections, and insights into student behavior, making learning more adaptive.
Valuing soft skills and continuous learning:
The demand for professional training and lifelong learning grew, leading platforms to offer modular courses and quick certificates aimed at the job market.
Challenges still present:
- Digital inclusion in regions with poor infrastructure
- Engagement and retention in 100% online courses
- Credibility and regulation of distance learning courses
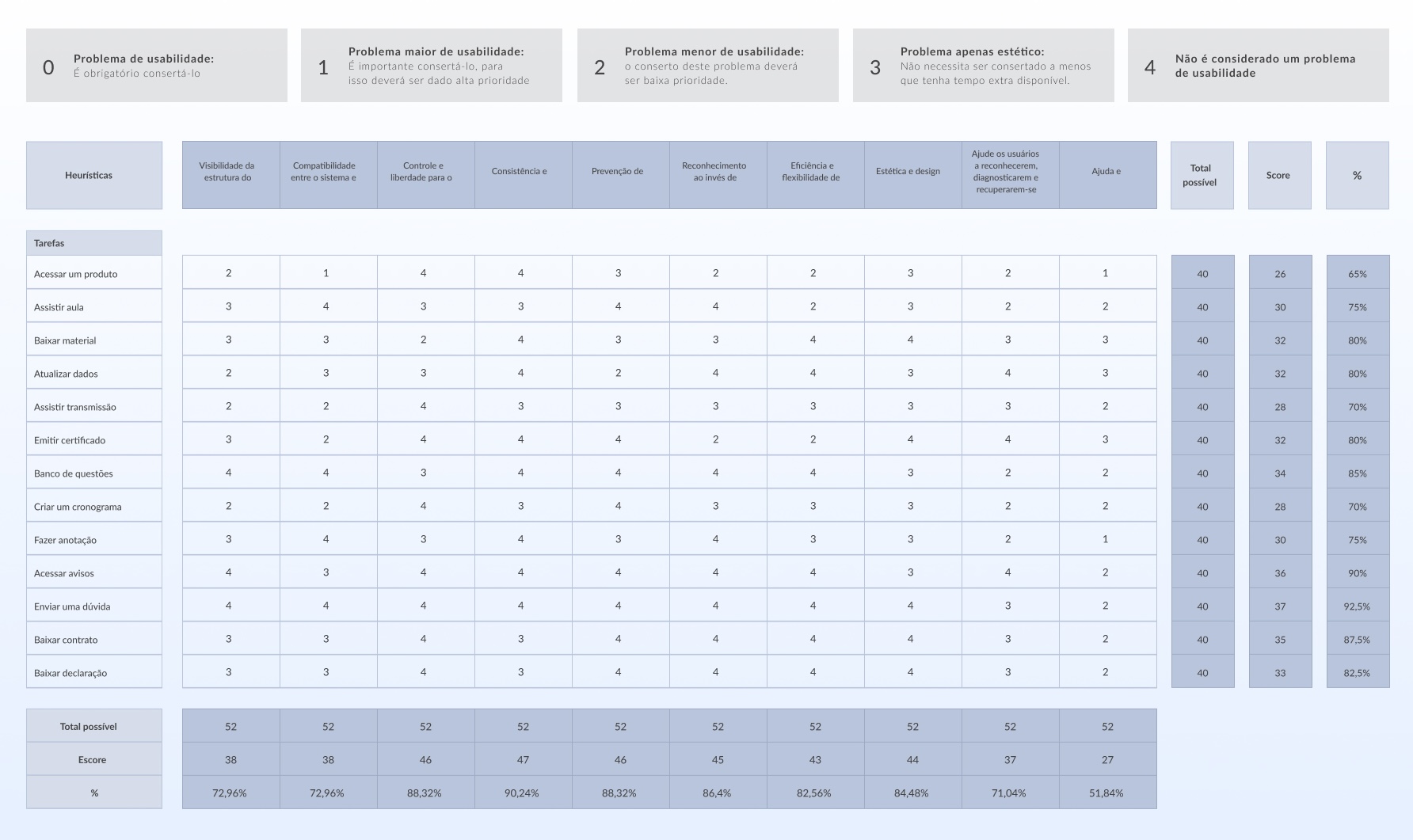
Heuristic Evaluation
A usability analysis was carried out on the current platform and the main flows and problems to be improved in the future were mapped in the portotypes and validated in the usability tests:
CSD Matrix
All points to be analyzed in the discovery have been process was mapped:
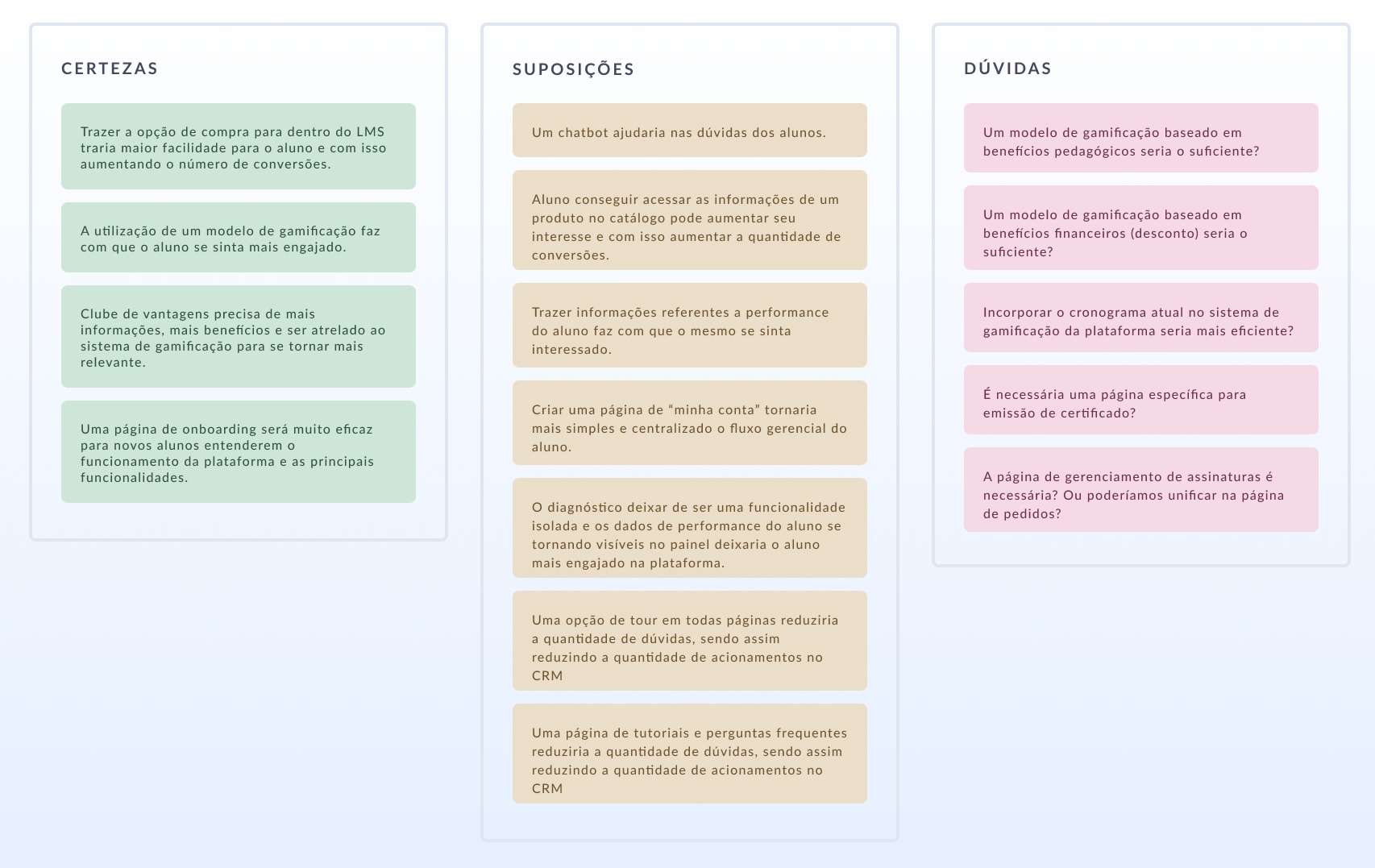
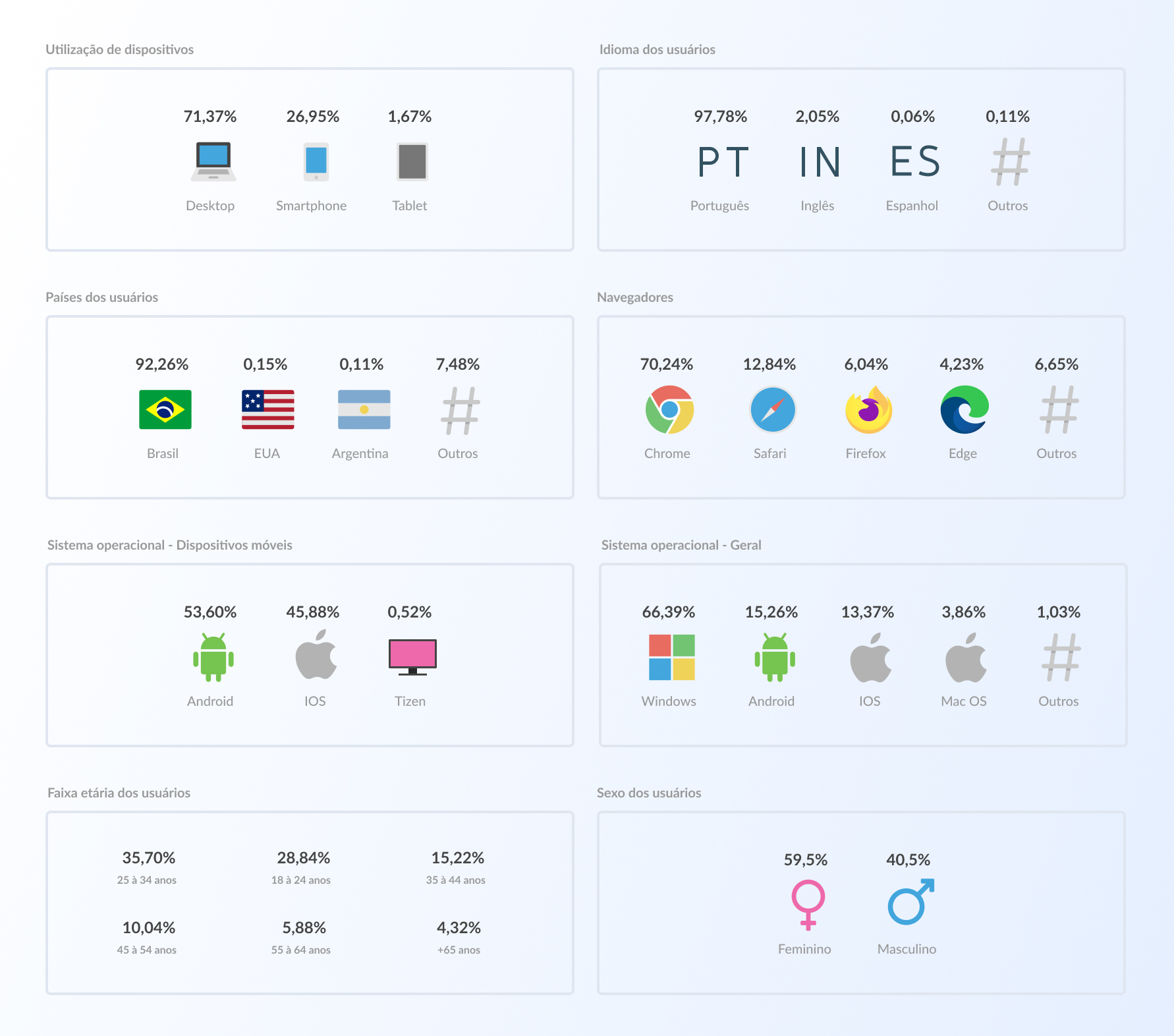
Desk research
A desk research was carried out to better understand the current market scenario of learning platforms, especially in the legal and public exams area. Current data from the CERS platform were also analyzed using tools such as Google Analytics and Hotjar, highlighting that:
Competitive benchmarking
The research analyzed the following platforms to understand what was already being done and how it could be improved and incorporated into the solution.

Analyzing results
The impact on society
Online learning platforms played a relevant role in democratizing quality legal education in Brazil, especially in a post-pandemic context where access to face-to-face education was still limited for much of the population.
Access to education in remote regions
The platform allowed students from regions far from major urban centers to prepare for public exams, OAB exams, and specialization courses with the same quality offered in major hubs.
Digital inclusion
With a simplified, responsive, and accessible interface, the new environment favored use on mobile devices and for audiences less familiar with technology, lowering barriers to online learning.
Social mobility
By facilitating access to solid legal training and approval in public exams, the new experience directly contributed to the professional and economic advancement of thousands of students who saw education as a real chance for life transformation.
Focus on student autonomy
The new structure promoted protagonism in learning, with tools that allowed students to monitor their performance, organize their studies, and build their own journey — strengthening the sense of responsibility and discipline, fundamental skills in personal development.
Valuing public and legal education
By strengthening the preparation of candidates for the public and legal sectors, the project also indirectly contributed to the training of professionals better prepared to act with ethics, knowledge, and social commitment.
Envisioning the solution
Brainstorming
Several ideas were raised, with the following selected for the initial version of the solution:
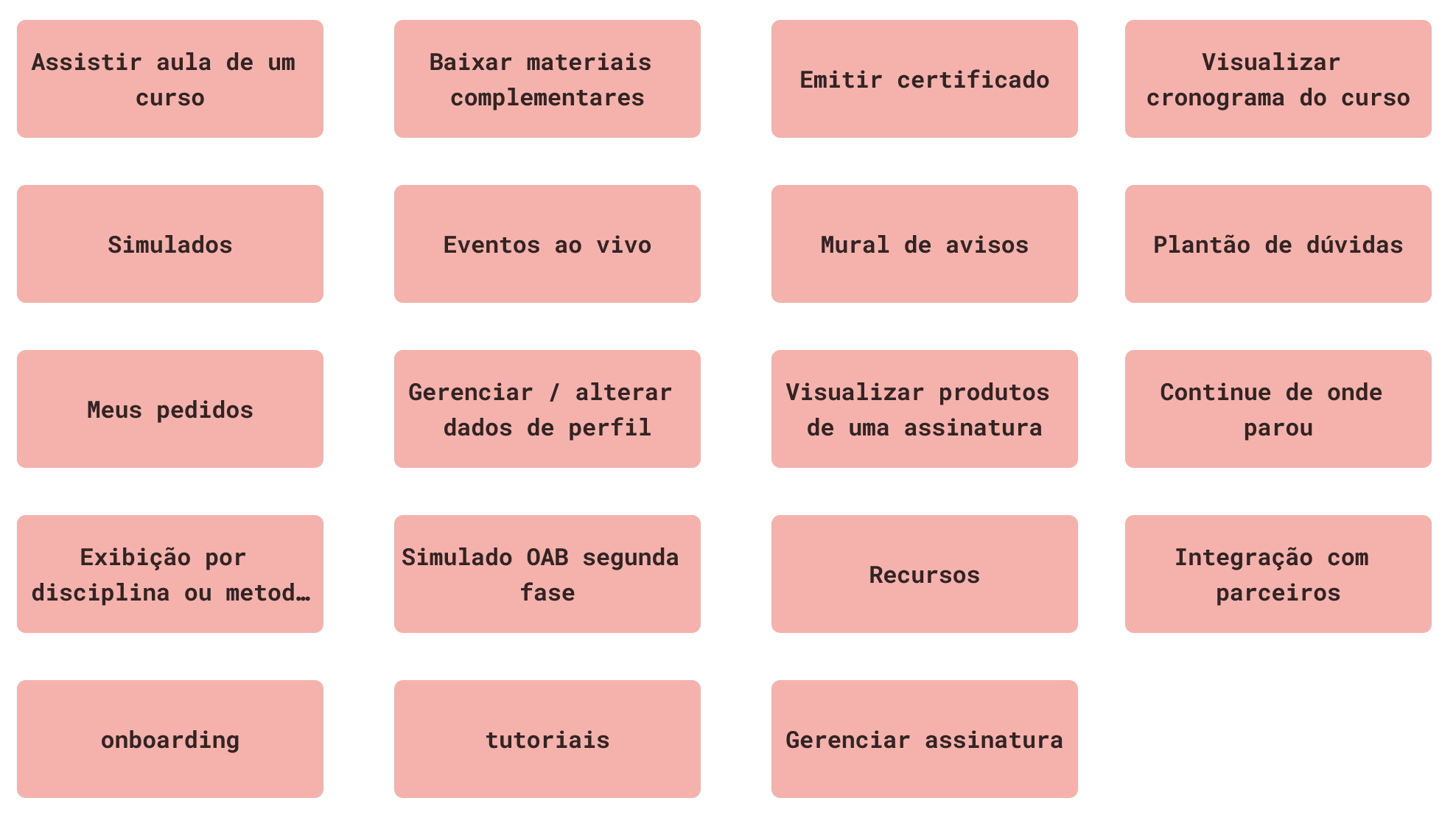
After all the analysis, it was possible to identify that the initial solution should be a responsive web platform and later a mobile version. Creating an app in the initial version would not be feasible due to the project's complexity and the limited development time.
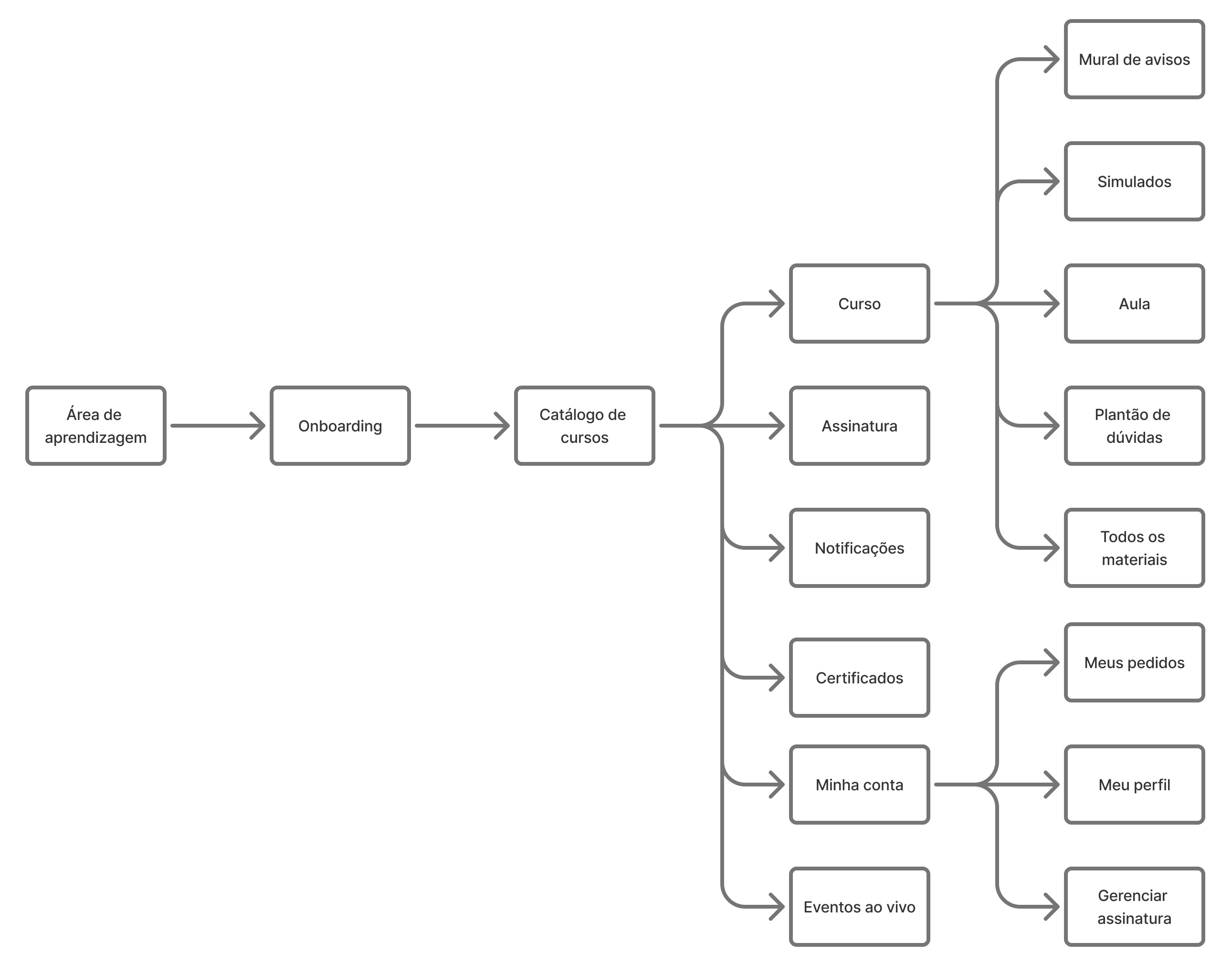
User flow
After mapping and organization, the user's navigation flow was created:
Moodboard
To contextualize the entire visual identity of the application, a board was created to be followed as an aesthetic/visual model for the creation of the styleguide.
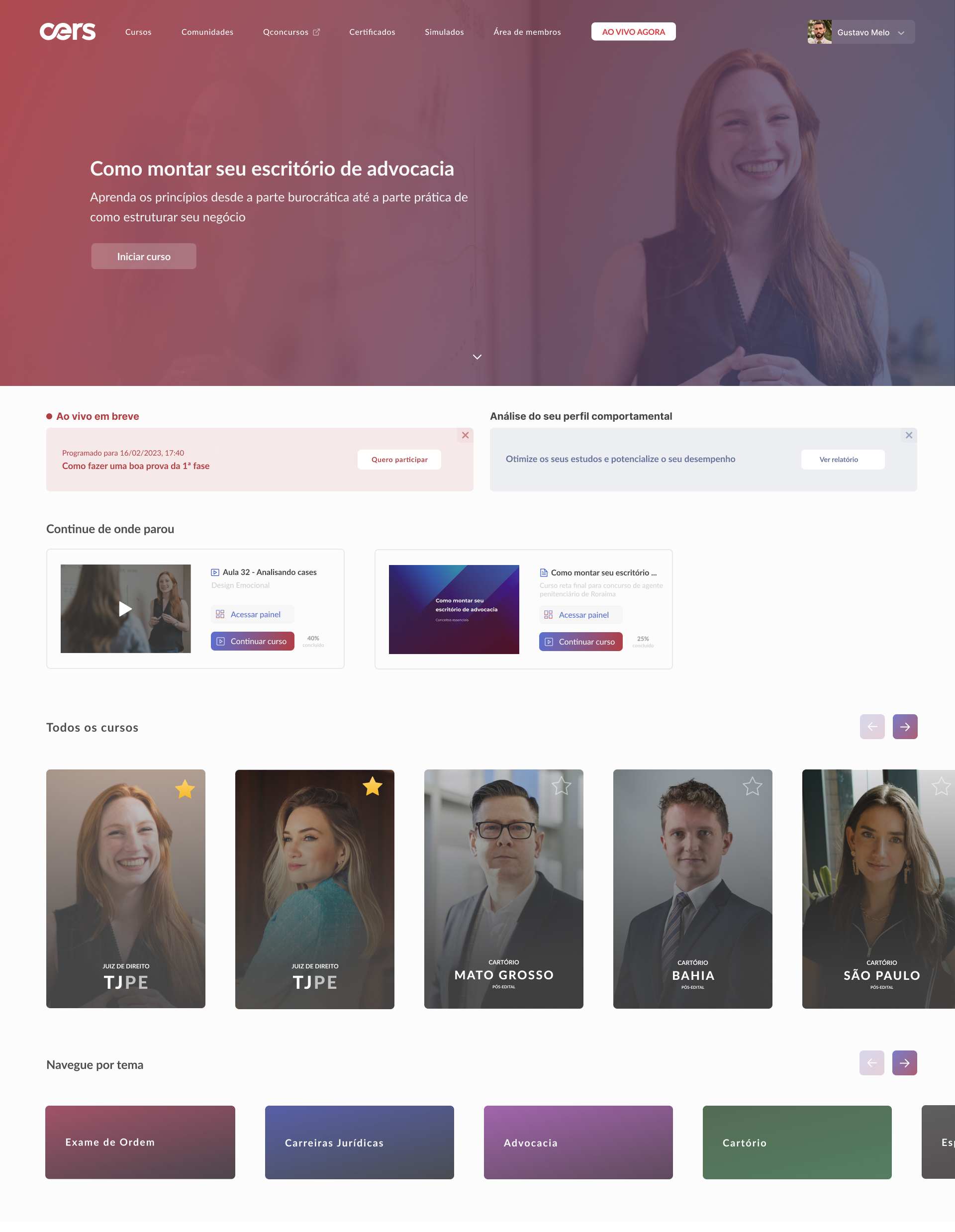
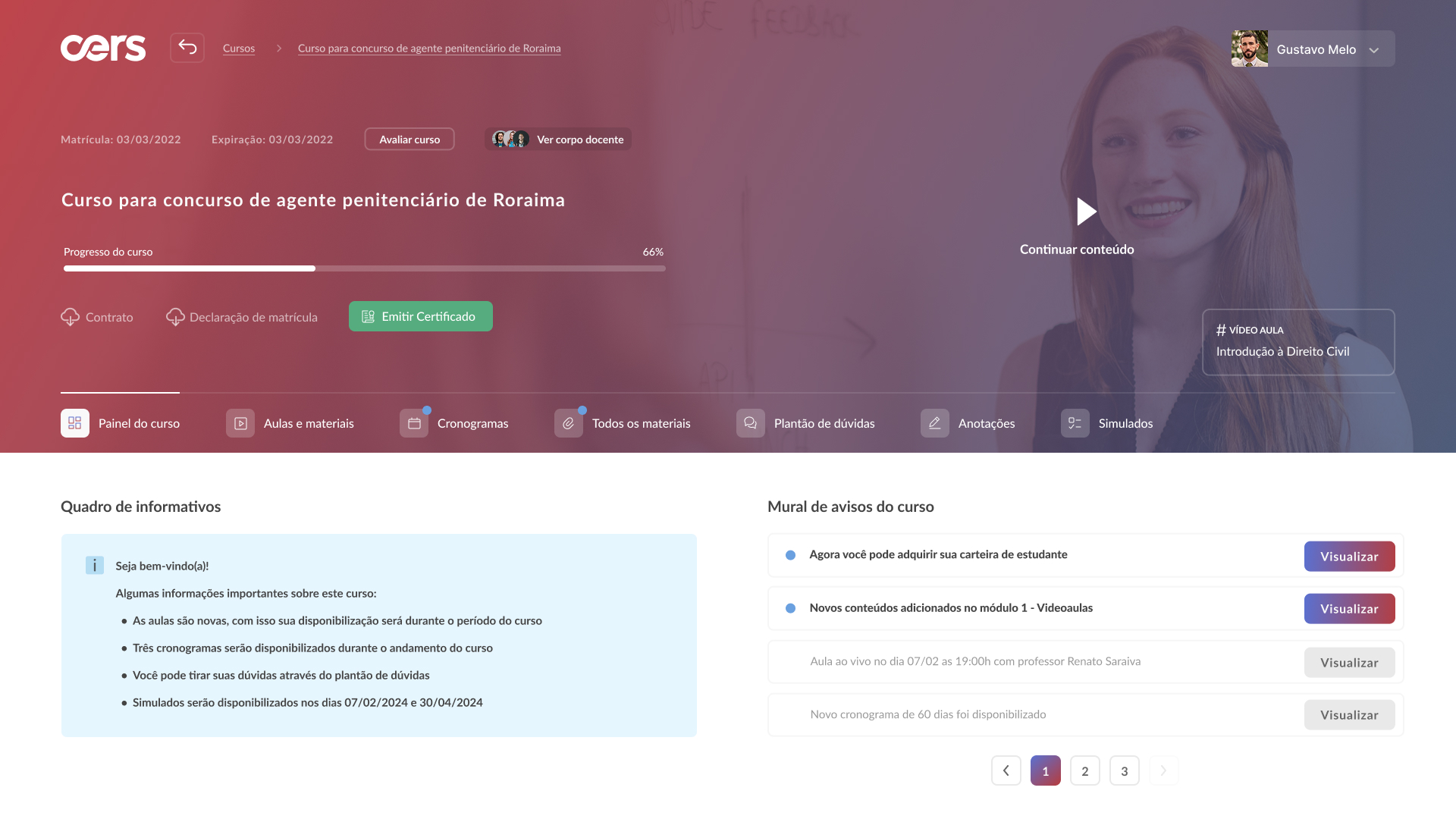
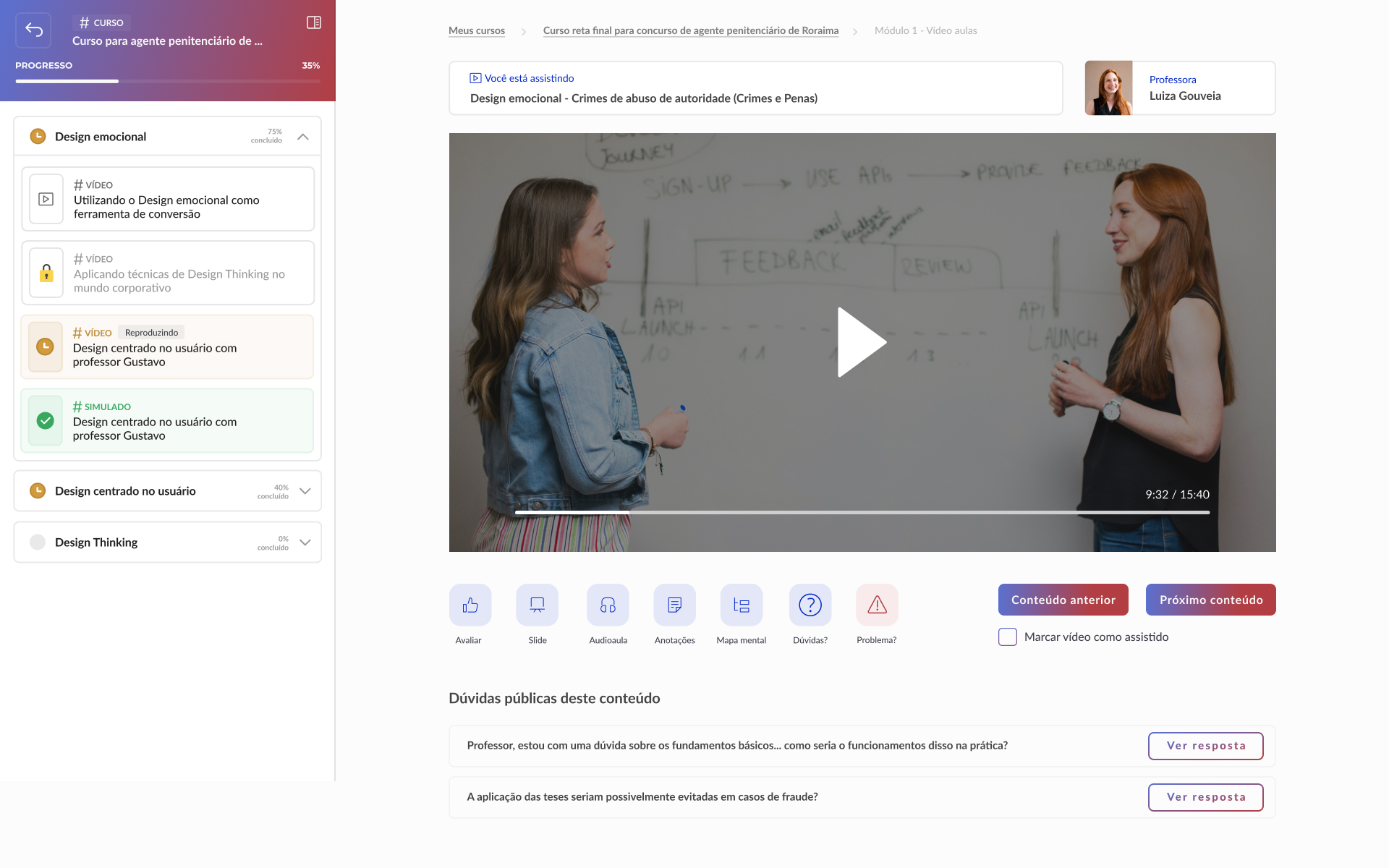
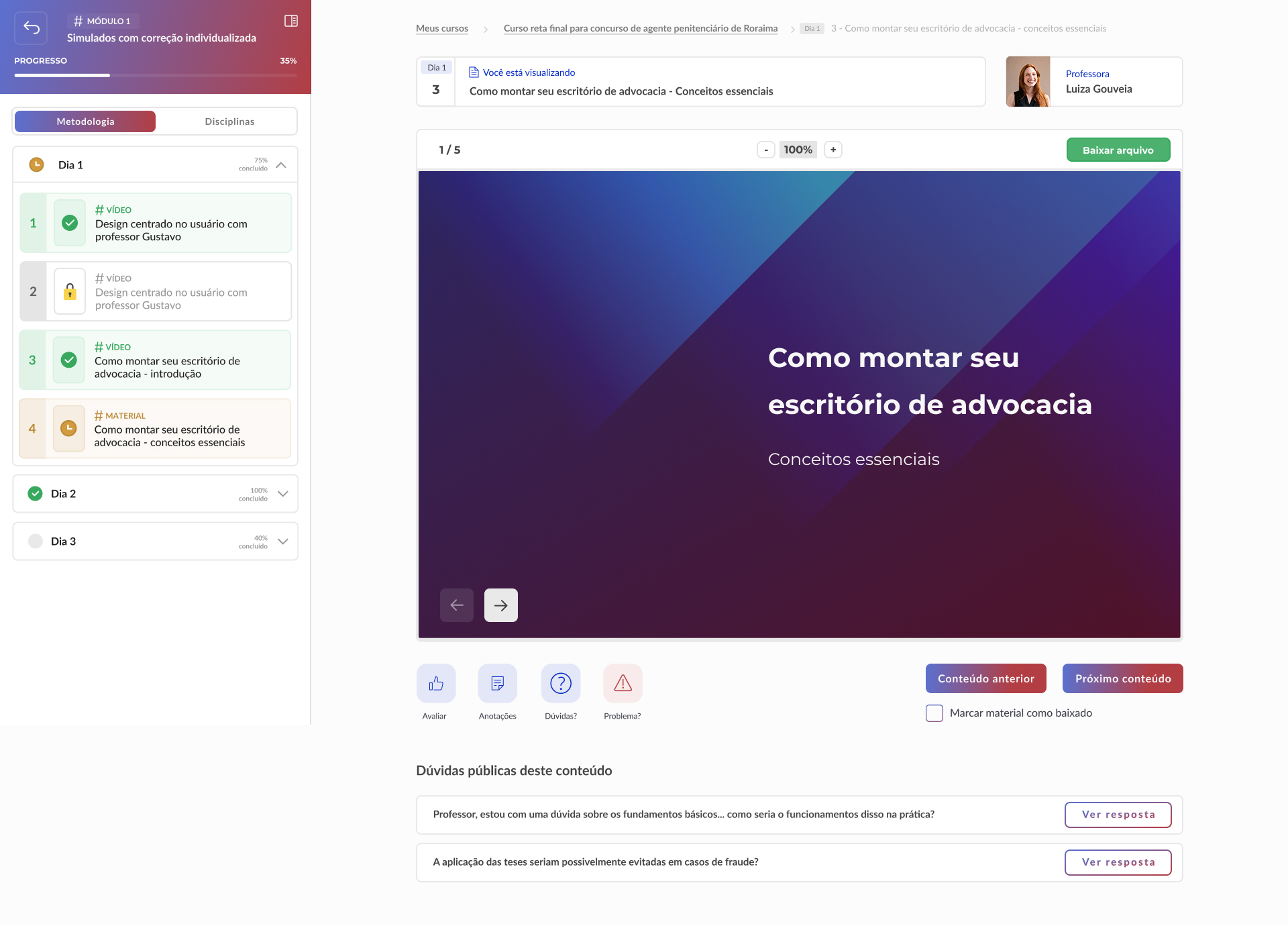
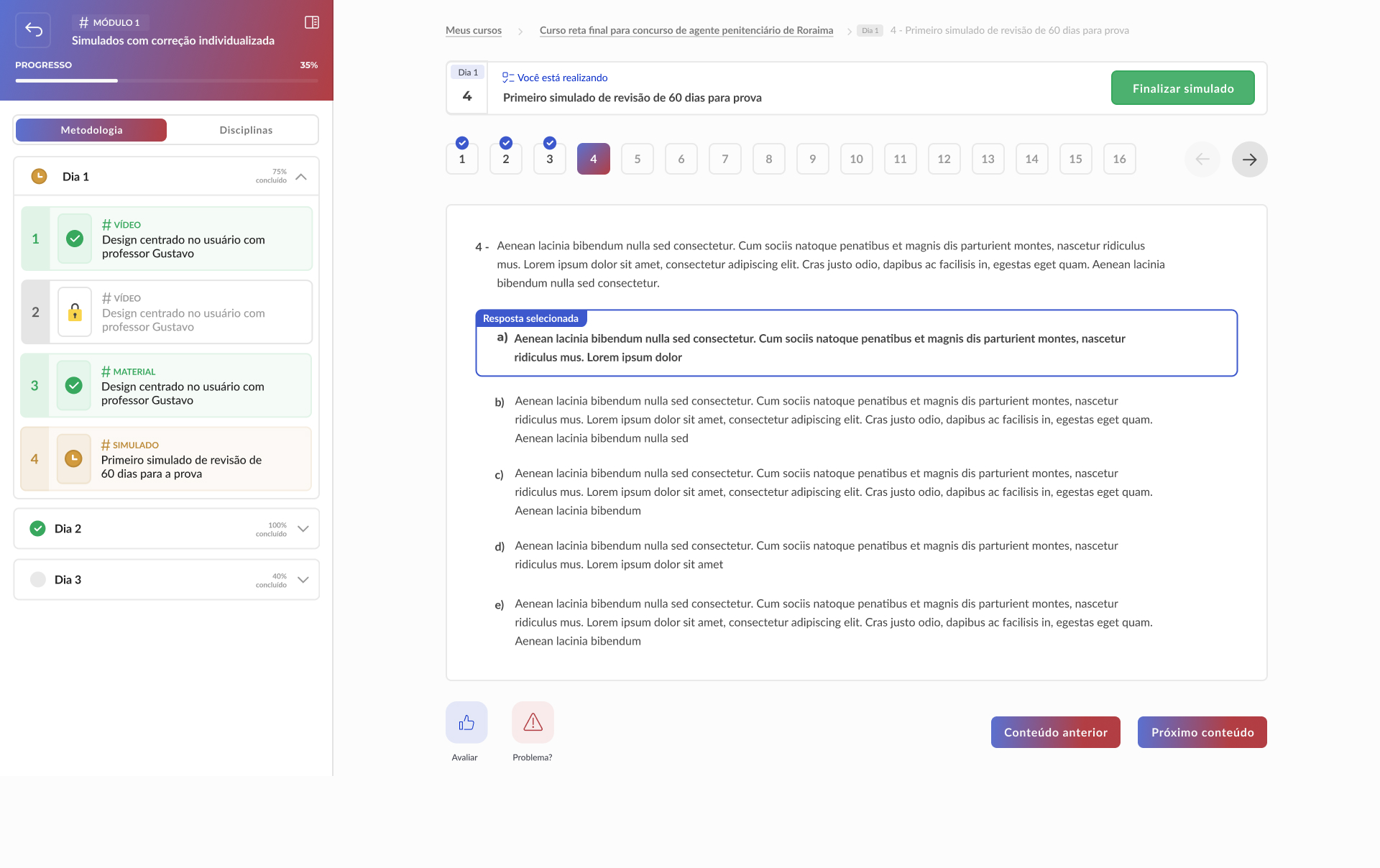
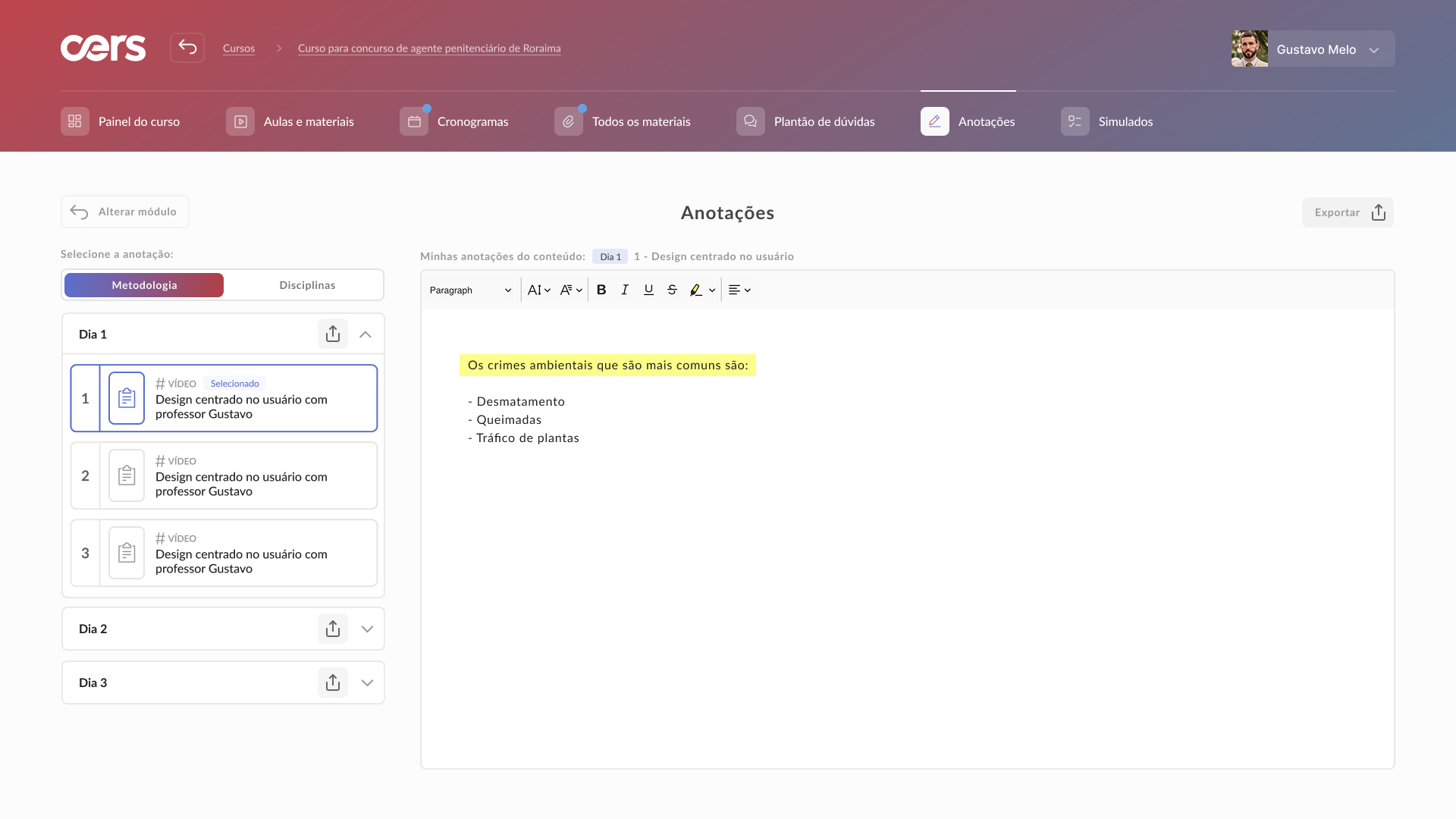
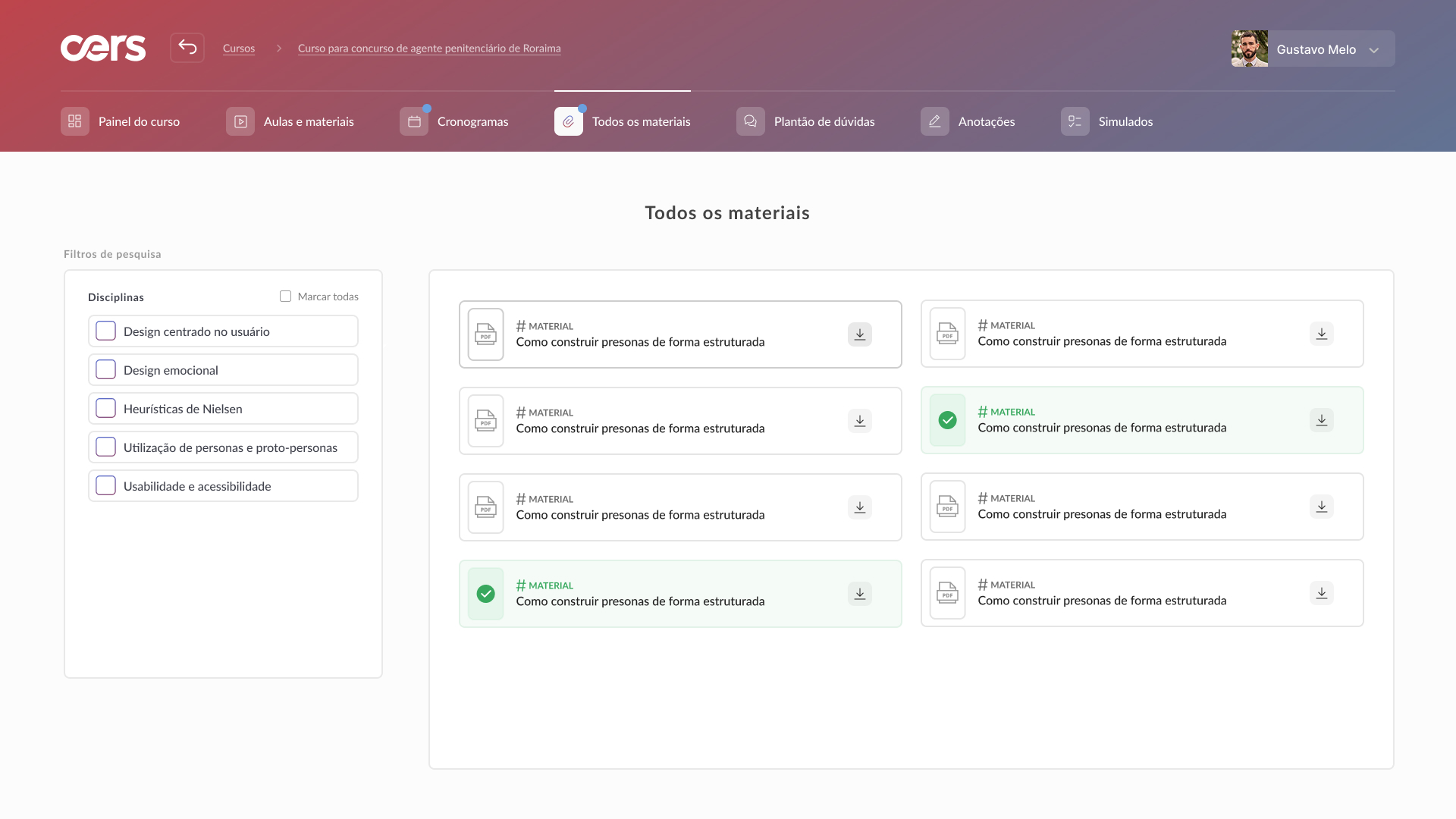
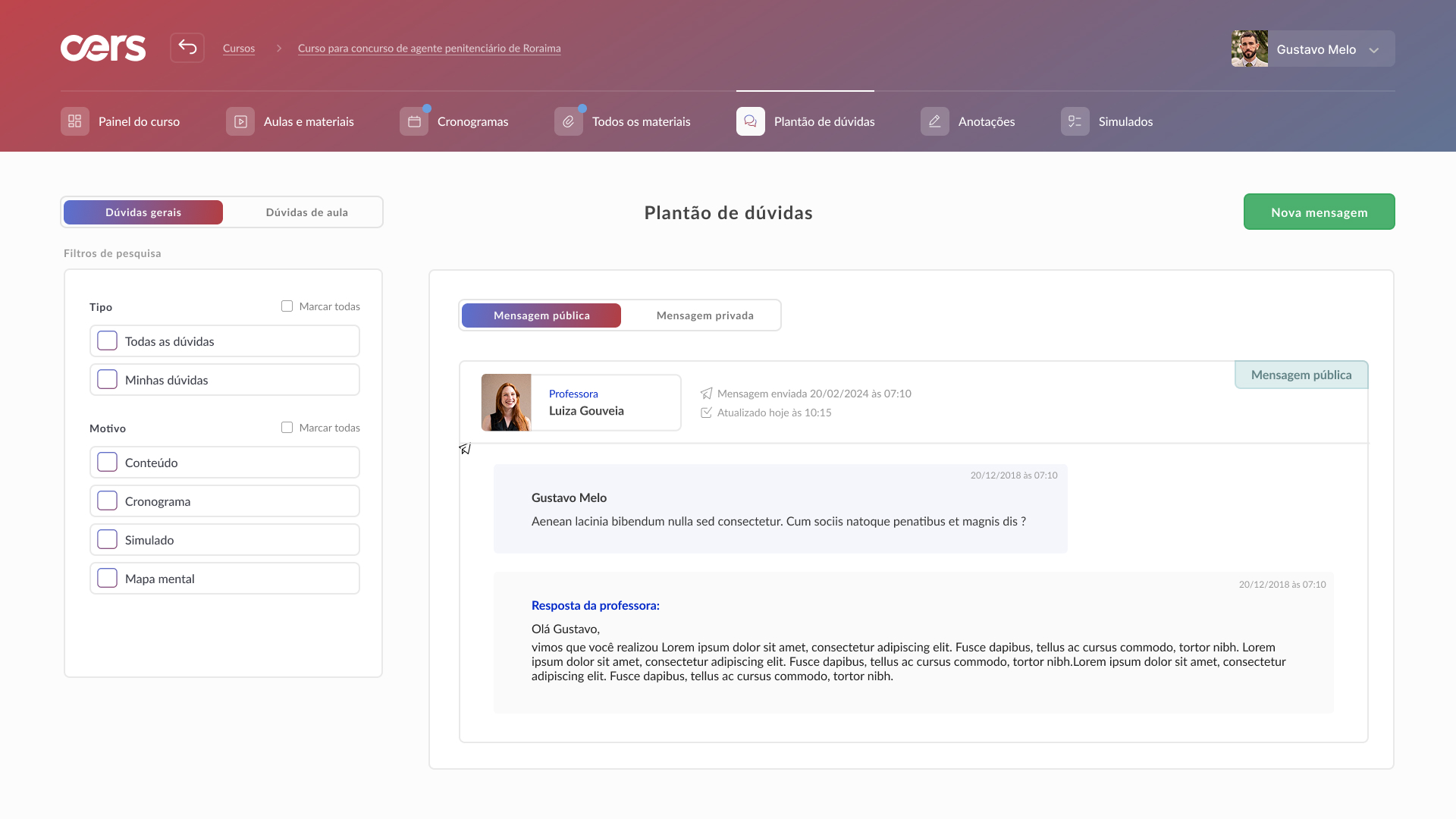
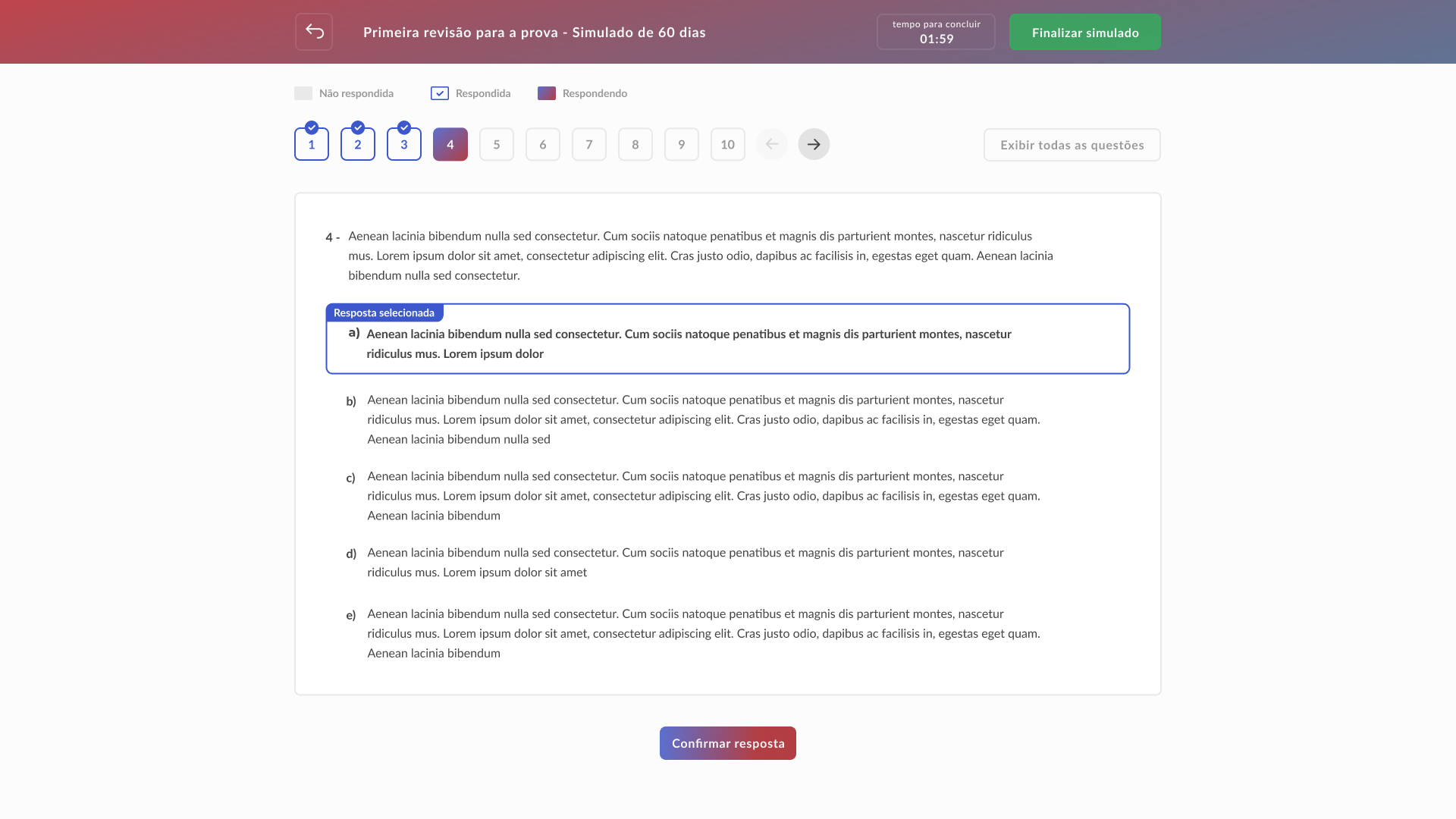
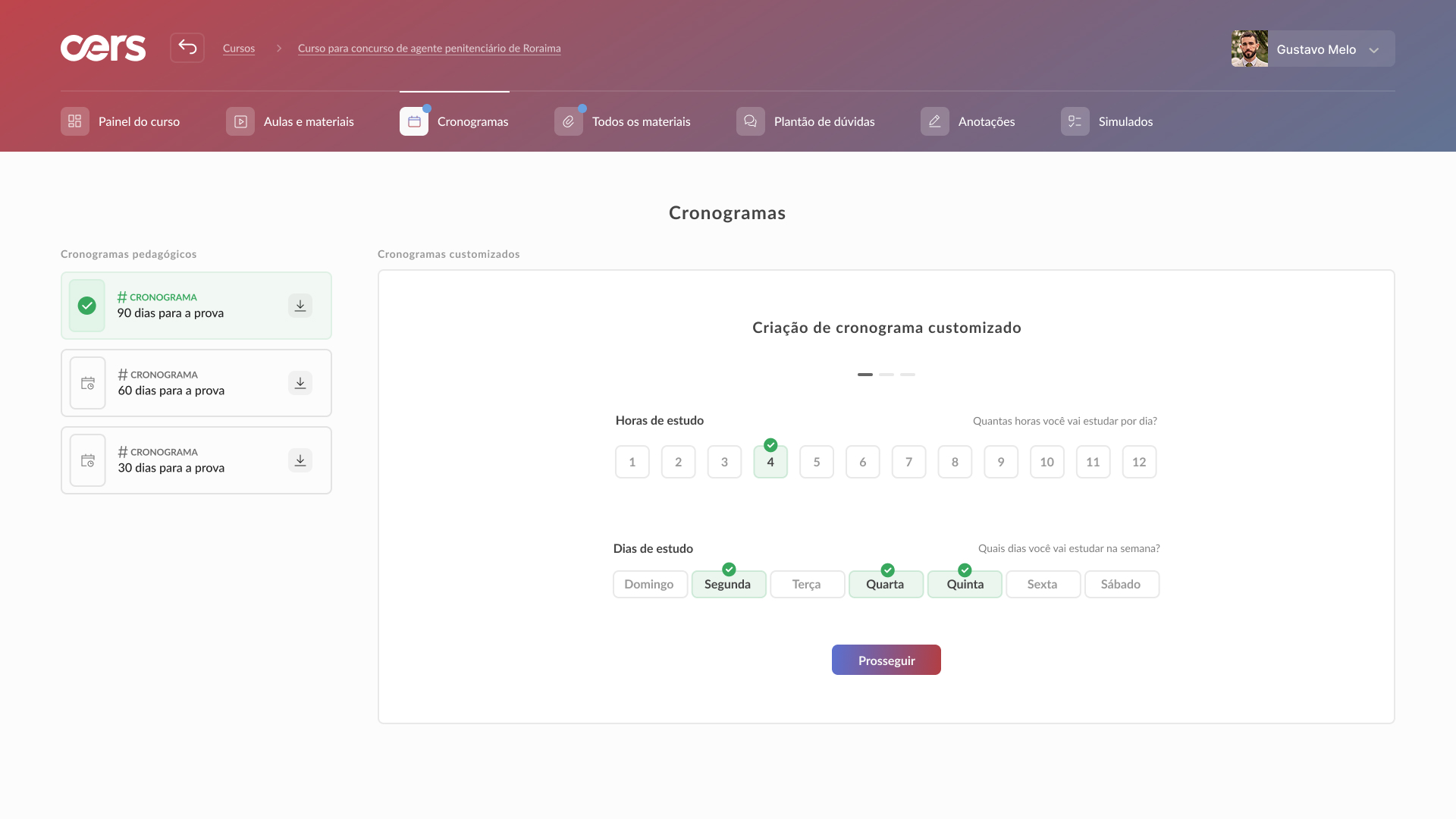
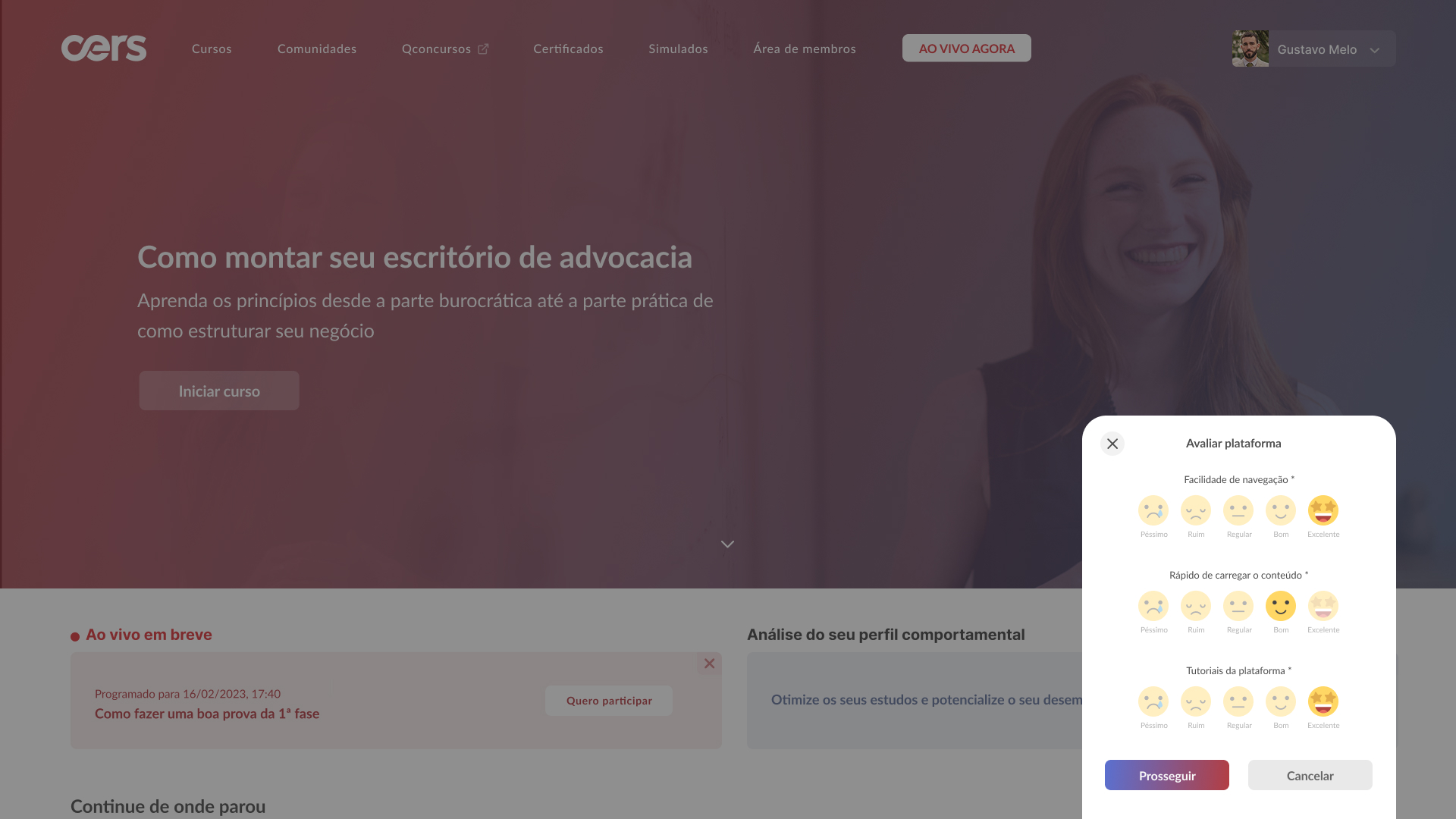
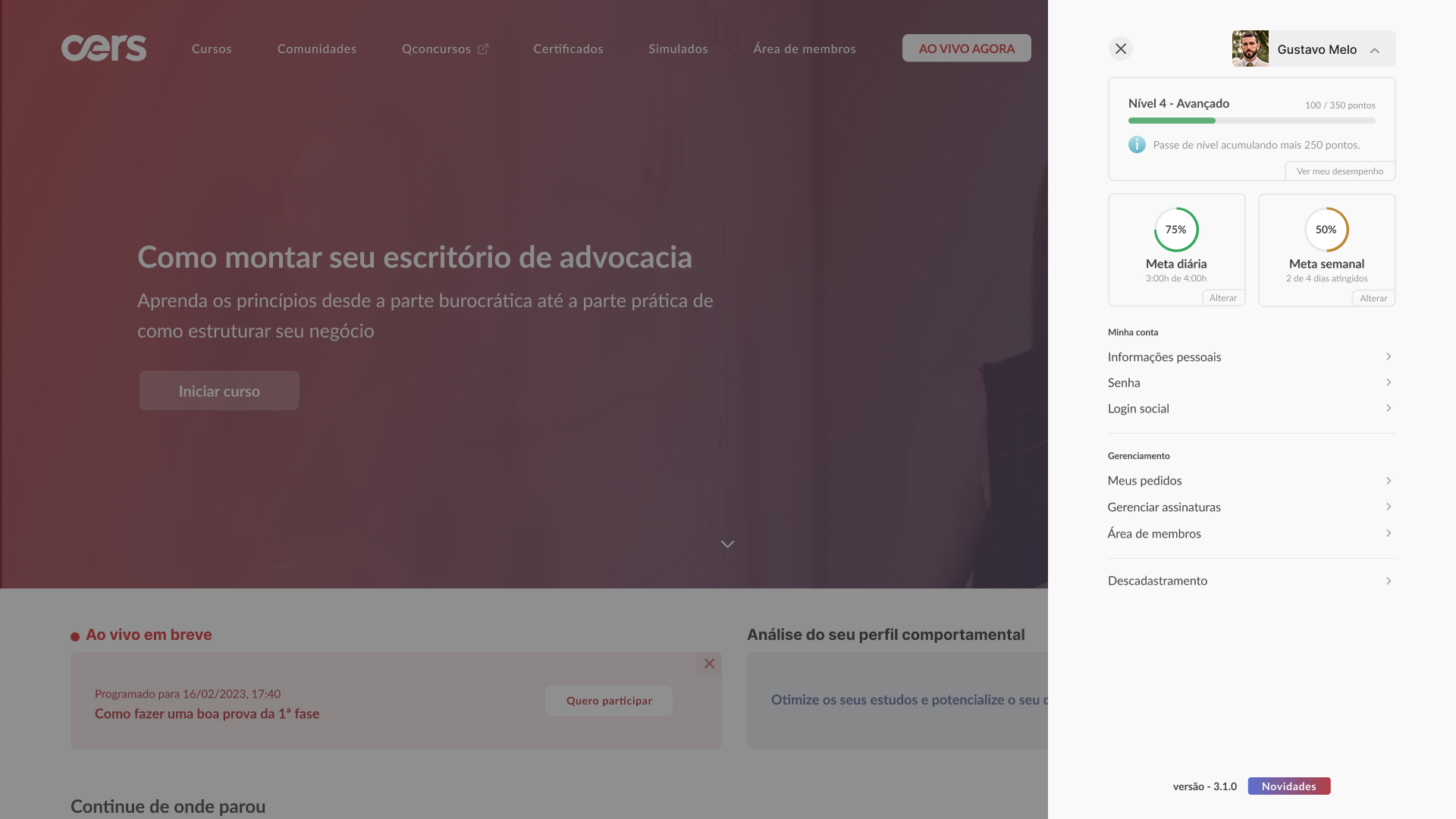
High-fidelity prototype
Taking into account the design system and insights from usability tests, it was possible to structure the high-fidelity prototype:
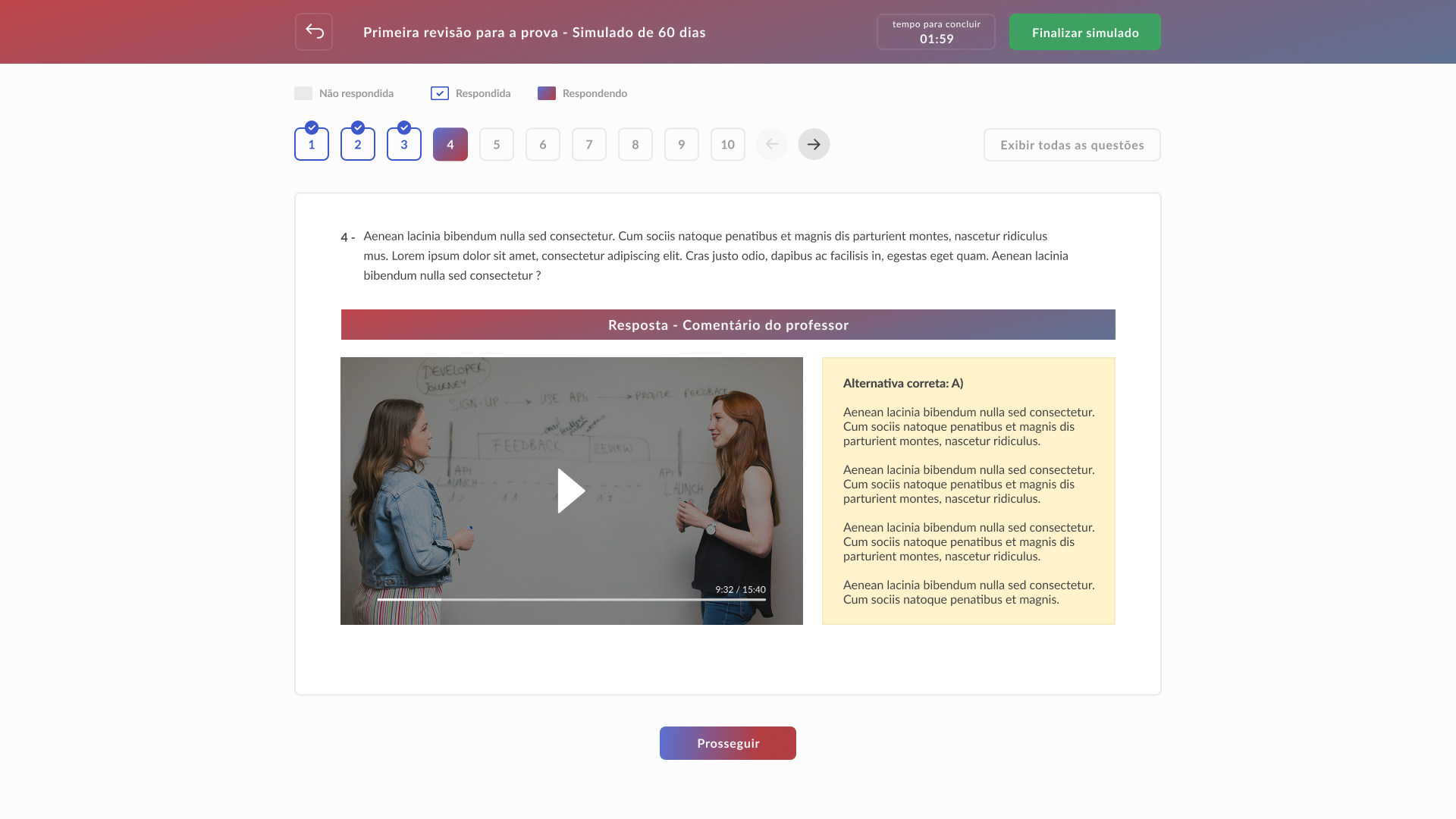
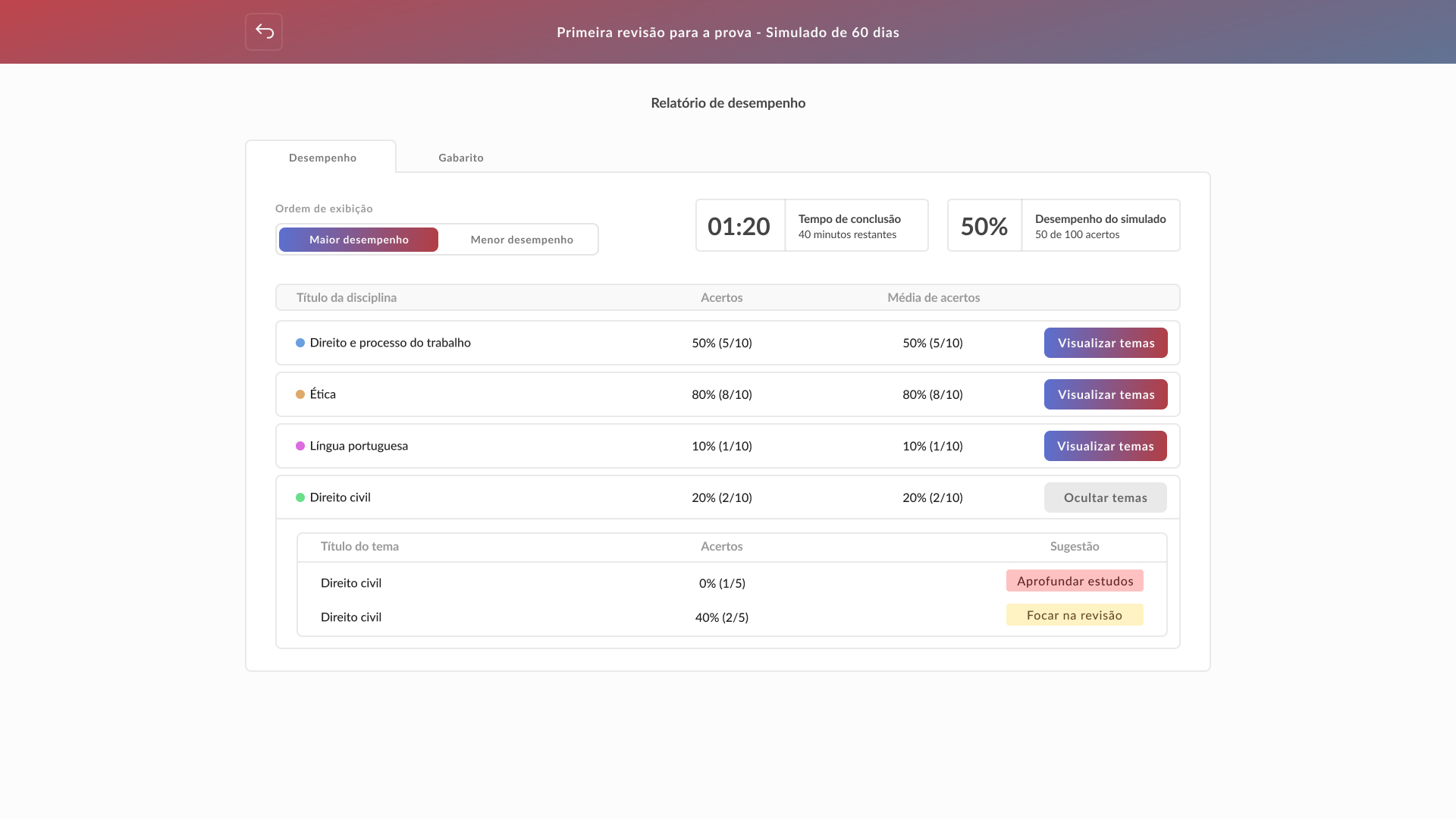
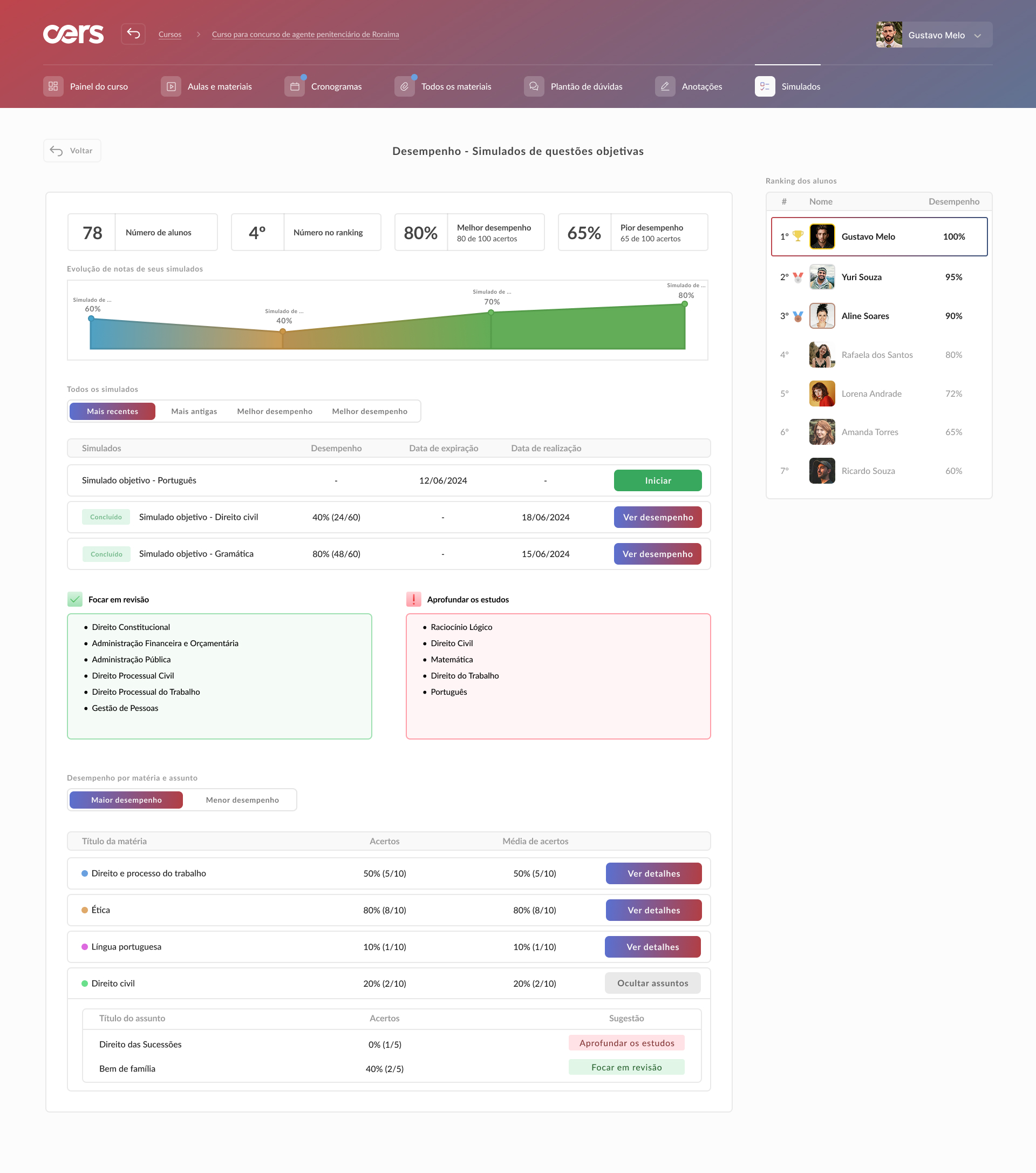
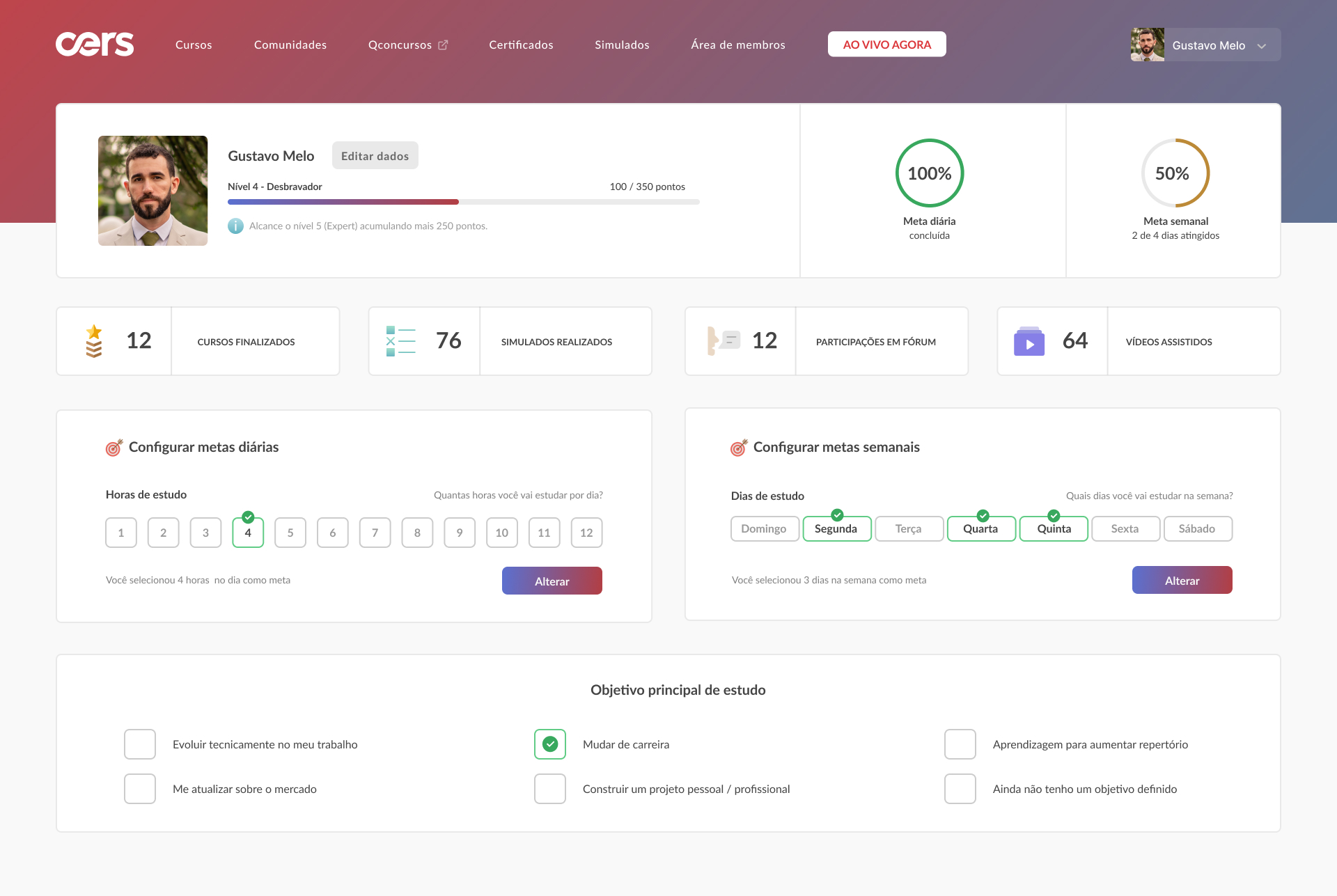
Conclusion and learnings
The new CERS Learning Area reinforced an essential principle: student engagement goes far beyond content — it involves experience. By putting the user at the center of the design process, it was possible to develop a more intuitive, fluid, and motivating environment.
Among the main learnings from the project, the following stand out:
Clarity and organization increase engagement:
Objective dashboards, well-structured learning paths, and clear progress visualization keep students motivated and moving forward.
Small improvements make a big difference:
Features such as resuming the video from where it left off, integrated materials, and smart filters directly impacted the time spent and return to the platform.
Autonomy generates commitment:
By allowing students to view their performance and manage their journey, the platform encouraged more active and continuous engagement.
Design and technology are allies of education:
The user-friendly interface, adapted to different devices, reduced friction and facilitated constant access to content, especially in unstructured study contexts.
The new platform has become not only a content delivery channel but a user-centered learning environment capable of transforming studying into a more productive, enjoyable, and effective experience.
Next project
Case study on the use of self-service kiosks in supermarkets
